验证数据展示
产品信息
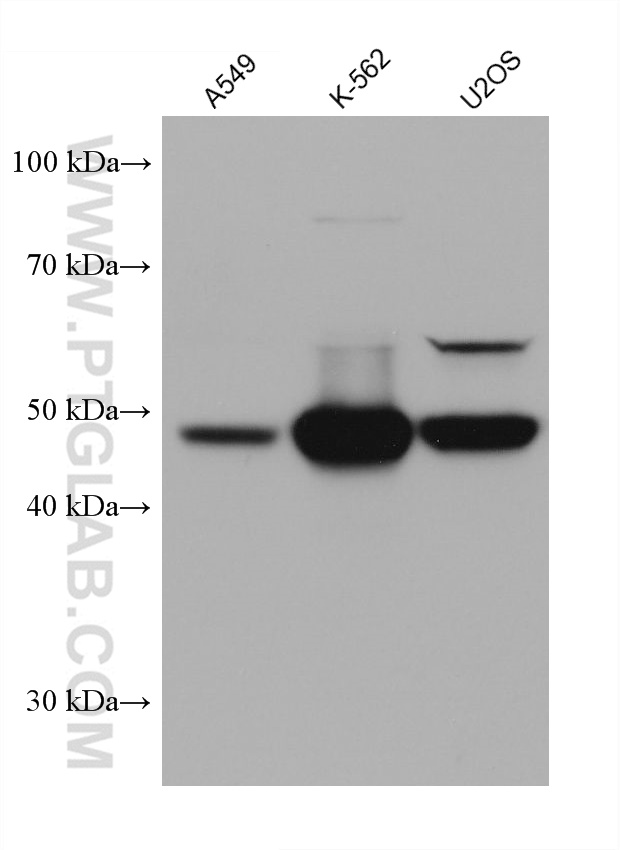
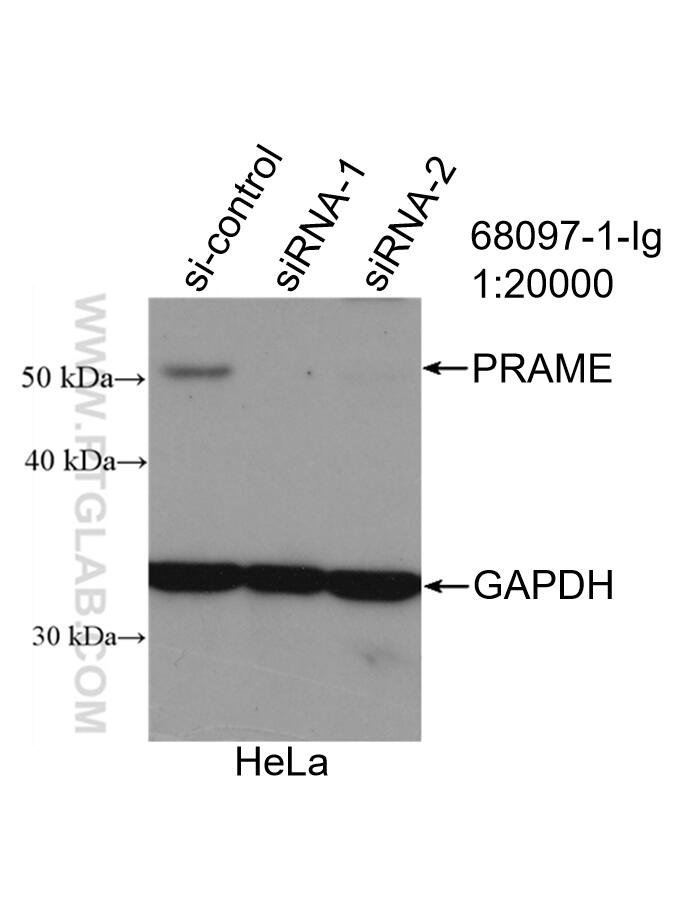
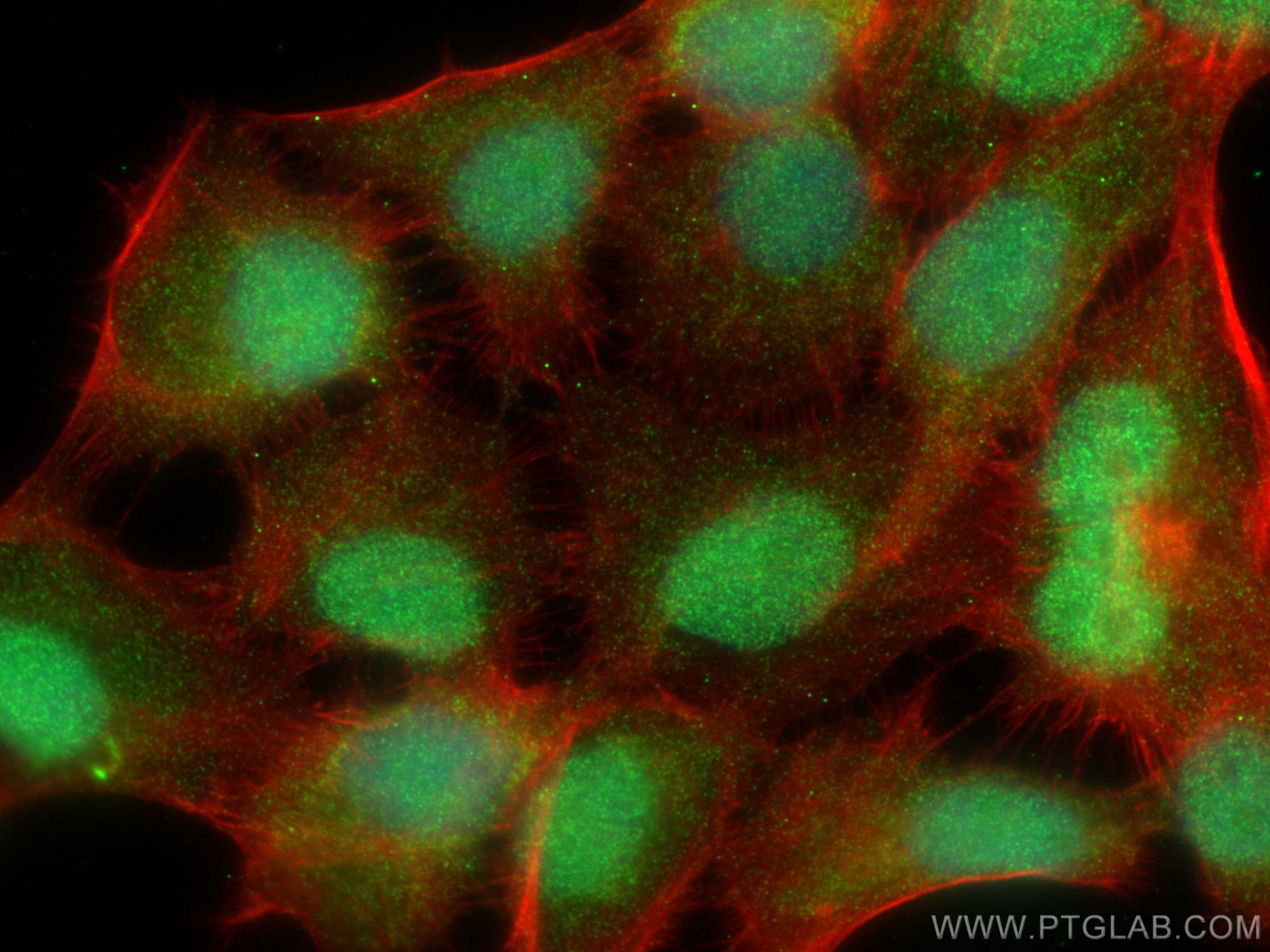
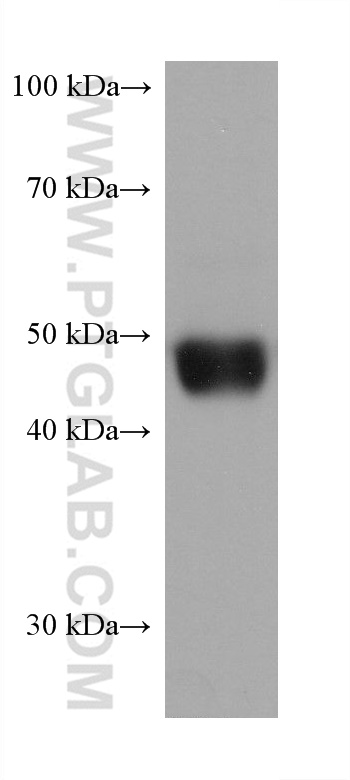
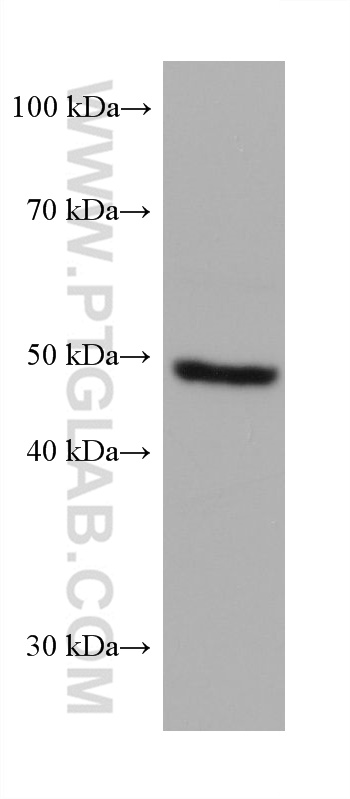
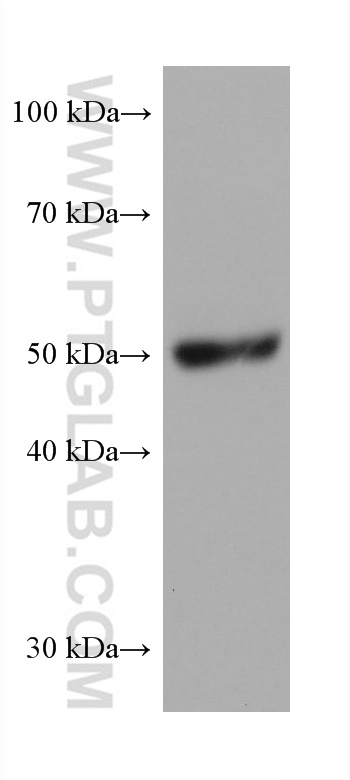
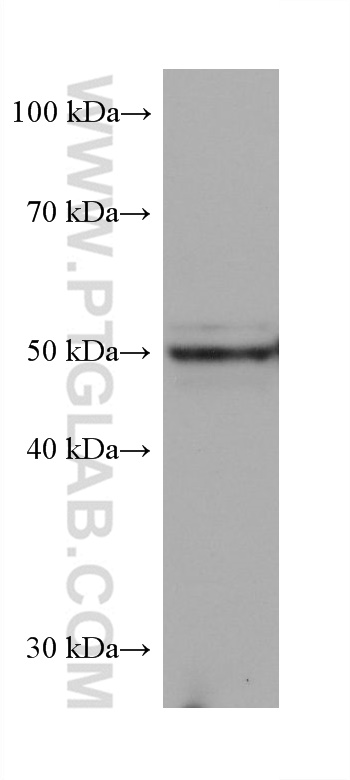
68097-1-PBS targets PRAME in WB, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with Human, mouse, rat samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | Human, mouse, rat |
| 免疫原 | PRAME fusion protein Ag1906 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Mouse / IgG2b |
| 抗体类别 | Monoclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | preferentially expressed antigen in melanoma |
| 别名 | MAPE, OIP 4, OIP4, Opa interacting protein 4, PRAME |
| 计算分子量 | 509 aa, 58 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 50 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC014074 |
| 基因名称 | PRAME |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 23532 |
| RRID | AB_2918834 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P78395 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
The PRAME (preferentially expressed antigen of melanoma) gene was previously shown to be overexpressed in ovarian/primary peritoneal serous carcinoma compared with malignant mesothelioma using gene expression arrays. It is considered a melanocyte differentiation antigen which is overexpressed in both solid and hematologic tumors. In normal tissue, a very low level of PRAME expression is found in normal testis, adrenals, ovary and endometrium. A high level of PRAME expression has been reported for several solid tumors, including ovarian cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer and melanomas, medulloblastoma, sarcomas, head and neck cancers, neuroblastoma, renal cancer, and Wilms'tumor. As a nuclear transcriptional repressor protein, PRAME binds to retinoic acid receptor a, thereby inhibiting retinoic acid induced differentiation, growth arrest, and apoptosis.