验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
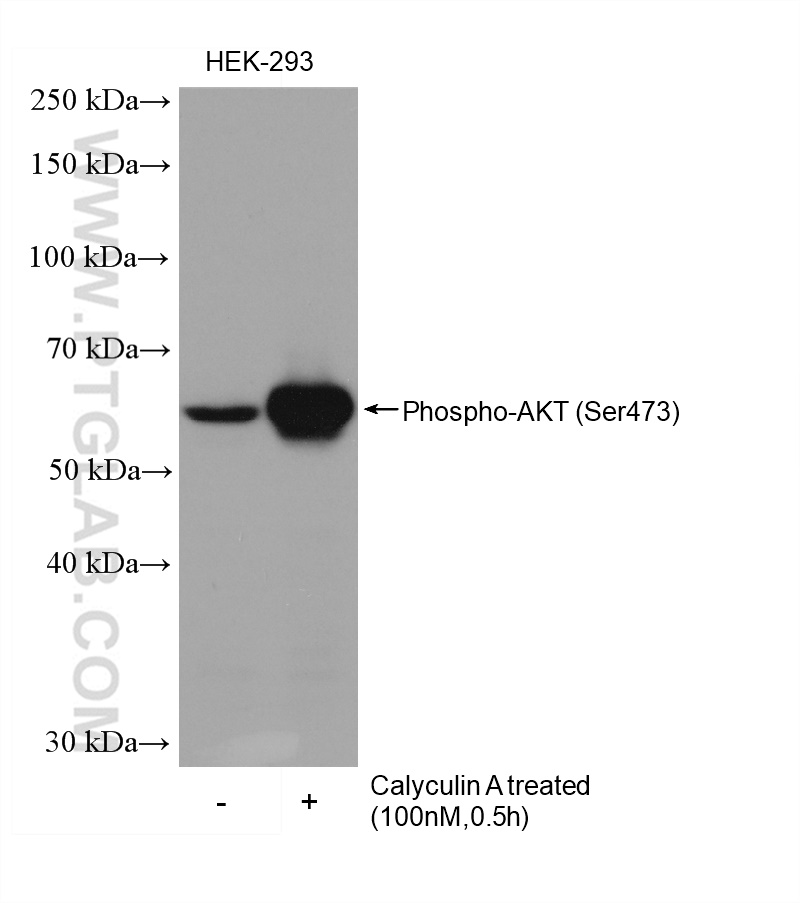
| Positive WB detected in | Calyculin A treated HEK-293 cells |
推荐稀释比
| 应用 | 推荐稀释比 |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
发表文章中的应用
| WB | See 1 publications below |
产品信息
HRP-66444 targets Phospho-AKT (Ser473) in WB applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB Application Description |
| 文献引用应用 | WB |
| 经测试反应性 | human, mouse |
| 文献引用反应性 | rat |
| 免疫原 |
Peptide 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Mouse / IgG1 |
| 抗体类别 | Monoclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1 |
| 别名 | AKT (Ser473), p AKT, p AKT (Ser473), p AKT Ser473, p-AKT |
| 观测分子量 | 60-62 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | NM_005163 |
| 基因名称 | AKT1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 207 |
| RRID | AB_3083816 |
| 偶联类型 | HRP |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P31749 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
背景介绍
1) What is AKT?
The serine/threonine kinase B AKT pathway (also known as the PI3K-Akt pathway) plays a vital role in the regulation of cellular processes, including cell proliferation, survival, and growth - processes that are essential for oncogenesis. Mutation of the regulator proteins PI3K and PTEN causes uncontrolled disruption within the PI3-kinase pathway, leading to the development of human cancers (1,2; see also AKT pathway poster for more details).
2) phospho-AKT and FAQs
A) What is the best way to normalize phosphorylated proteins analyzed by western blot?
Normalize phospho-AKT and total AKT with your loading control (e.g. Actin, tubulin), then calculate the phospho/total ratio using these normalized values.
Put more simply:
1. Calculate the ratio of band intensities of a phospho-AKT band: the loading control.
2. Calculate the ratio of band intensities of total AKT: loading control.
3. Divide ratio obtained #1 by #2 to obtain a normalized value for comparison among different conditions. This procedure allows one to distinguish between a change in AKT expression and a change in the ratio of phospho-AKT.
* If you are looking at the differences in a phospho-AKT expression resulting from an experimental condition (e.g., knockdown), you should also show the expression of total AKT to distinguish between a change in AKT expression (transcription/translation level) and a change in the AKT phosphorylation status.
B) What is the observed molecular weight for AKT and phospho-AKT?
Molecular Weight AKT - 56 kDa
Molecular Weight phospho-AKT - 60 kDa (Figure 1)

Figure 1. WB: HEK-293 cell lysate was subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with 60203-2-Ig (AKT antibody) and 66444-1-Ig (AKT-phospho-S473 antibody) at a dilution of 1:4000 incubated at room temperature for 1.5 hours.
C) Are there any special WB conditions to optimize staining of a phospho-AKT?
Since this is a phosphorylated protein, 5% BSA is recommended over non-fat milk as a blocking agent.
D) What are good positive and negative controls for a phospho-AKT?
- Positive Control: HEK293 cells
- Negative Control: Treatment with PI3K inhibitors (e.g. wortmannin)
E) What species does this antibody react with?
Our internal testing has confirmed that it reacts with the human and mouse forms of phospho-AKT.Reactivity with the human form is also supported by the literature's citations of this antibody.
References:
1. Perturbations of the AKT signaling pathway in human cancer.
2. Targeting the PI3K-Akt pathway in human cancer: rationale and promise.
实验方案
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for HRP Phospho-AKT (Ser473) antibody HRP-66444 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |