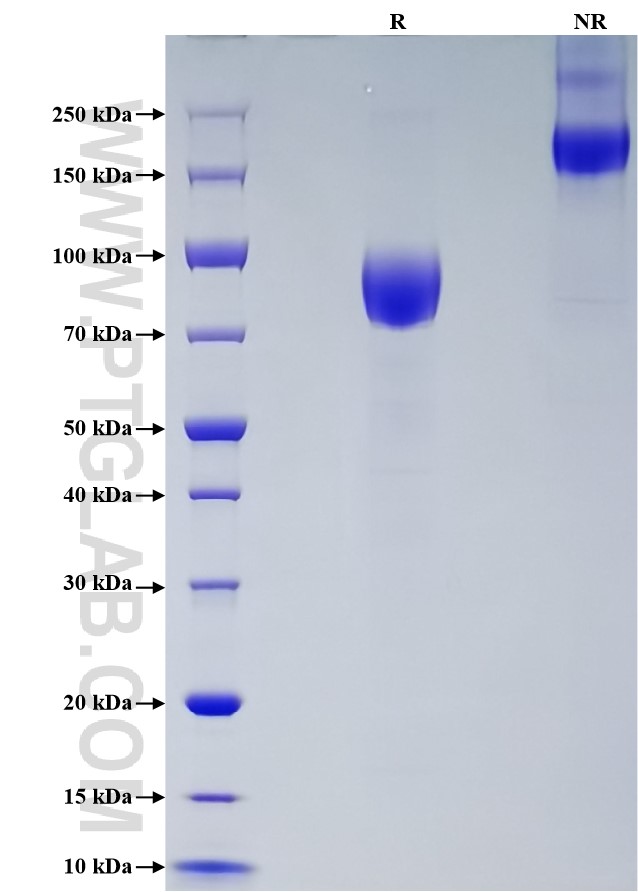
Recombinant Human CD200R1 protein (hFc Tag, Myc Tag, His Tag)
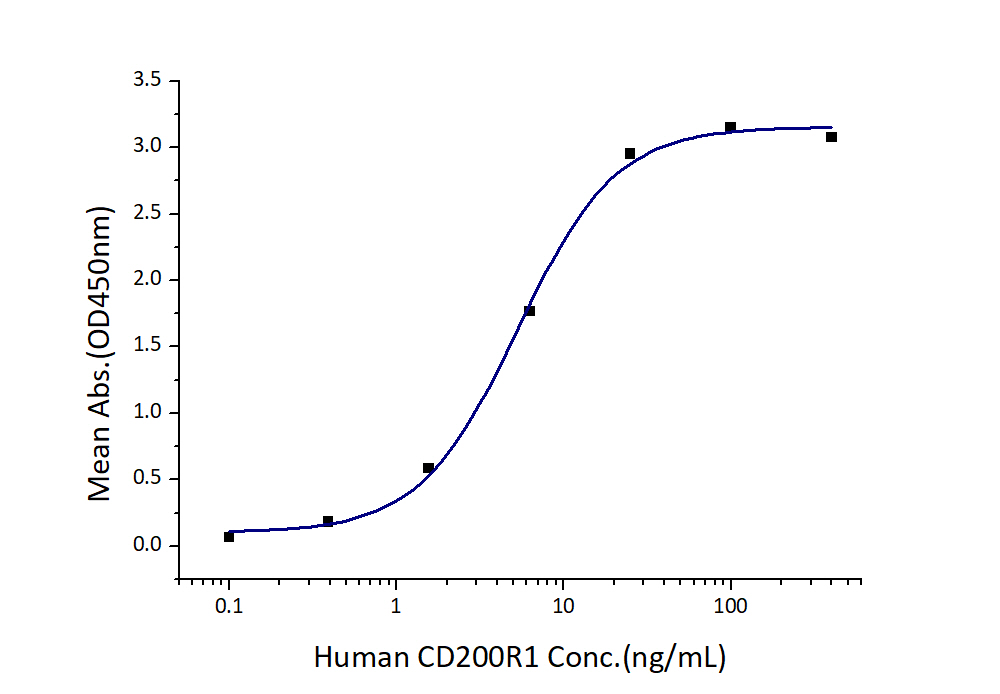
ED50
3-10 ng/mL
Species
Human
Purity
>95 %, SDS-PAGE
GeneID
131450
Accession
NP_620161.1
验证数据展示
Technical Specifications
| Purity | >95 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin Level | <1.0 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Biological Activity |
Immobilized Human CD200 (Myc tag, His tag) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human CD200R1 (hFc tag, Myc tag, His tag) with a linear range of 3-10 ng/mL. |
| Source | HEK293-derived Human CD200R1 protein Ala27-Leu266 (Accession# NP_620161.1) with a human IgG1 Fc tag, a Myc tag, a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Predicted Molecular Mass | 55.3 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 70-100 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
CD200R1 encodes a receptor for the OX-2 membrane glycoprotein, an Ig superfamily transmembrane glycoprotein expressed on the surface of myeloid cells; it can also be induced in certain T-cell subsets. CD200R1 interacts with CD200, which is also an Ig superfamily transmembrane glycoprotein, to down regulate myeloid cell functions. Mouse studies of a related gene suggest that this interaction may control myeloid function in a tissue-specific manner. CD200 is expressed on the surface of a variety of cells including neurons, epithelial cells, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, lymphoid cells, and astrocytes. The regulation of CD200R1 signaling can occur by posttranslational modification—namely, phosphorylation of tyrosines in the CD200R1 cytoplasmic tail—or by the inducible expression or downregulation of either CD200R1 or CD200.
References:
1. Timmerman LM., et al. (2021) PLoS One. 29;16(3):e0244770. 2. Lin S., et al. (2020) Eur J Neurol. 27(7):1224-1230. 3. Blom LH., et al. (2017) Allergy. 72(7):1081-1090. 4. Fraser SD., et al. (2016) Sci Rep. 8;6:38689. 5. Sun H., et al. (2016) Immunol Lett. 178:105-13. 6. Caserta S., et al. (2012) PLoS One. 7(4):e35466. 7. Wright GJ., et al. (2000) 13(2):233-42.