验证数据展示
产品信息
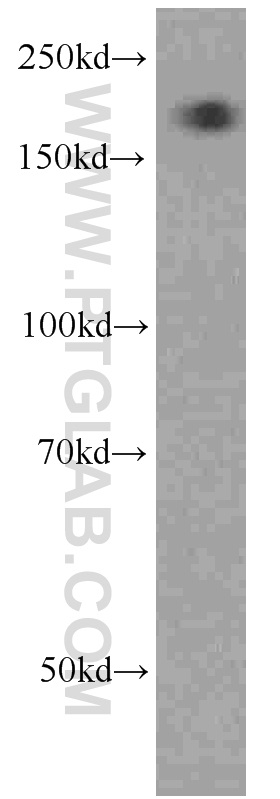
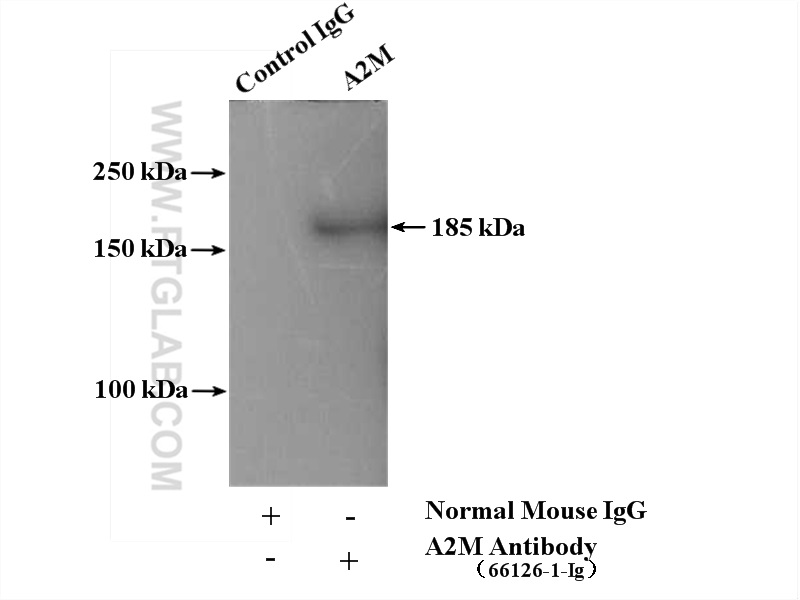
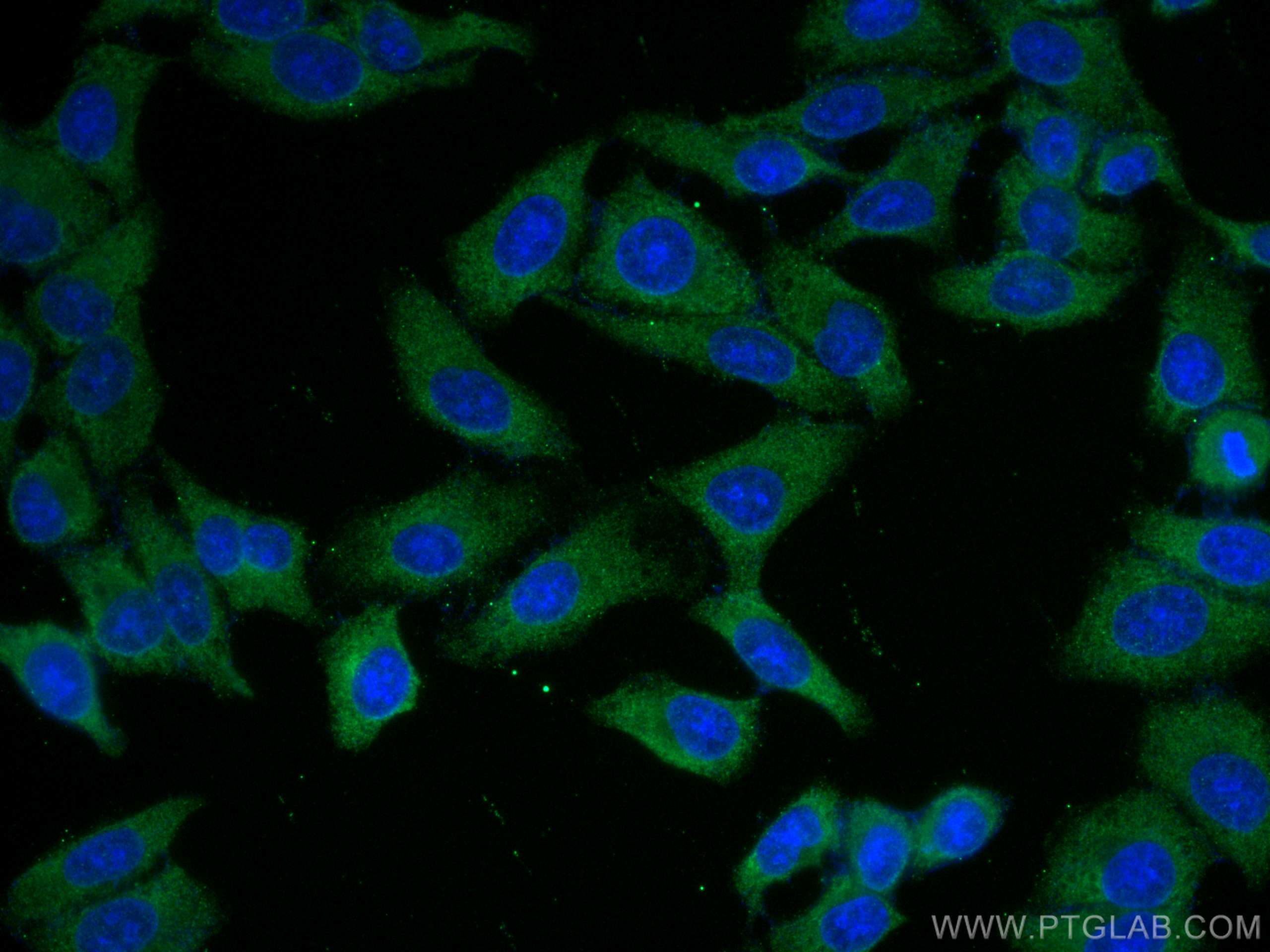
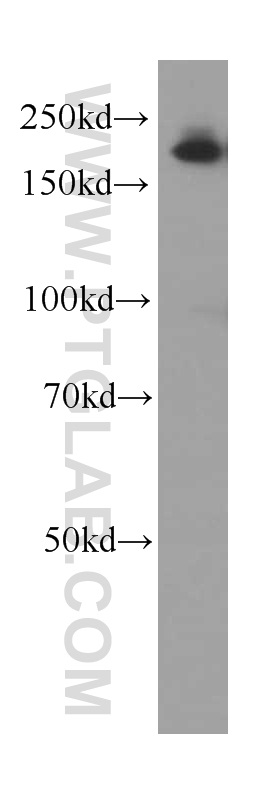
66126-1-PBS targets Alpha-2-Macroglobulin in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human |
| 免疫原 | Alpha-2-Macroglobulin fusion protein Ag19245 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Mouse / IgG2a |
| 抗体类别 | Monoclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | alpha-2-macroglobulin |
| 别名 | A2M, Alpha 2 M, alpha 2 macroglobulin, Alpha-2-Macroglobulin, CPAMD5, FWP007, S863 7, α-2M |
| 计算分子量 | 1474 aa, 163 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 185 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC040071 |
| 基因名称 | Alpha 2 Macroglobulin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2 |
| RRID | AB_2881525 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P01023 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS Only |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
alpha-2-macroglobulin, also known as α2-macroglobulin (α2M and A2M), is a protein abundant in the plasma of vertebrates and several invertebrates. A2M is an evolutionarily conserved arm of the innate immune system. It also mediates the proliferation of T cells and macrophages. A2M acts as a nonspecific protease inhibitor involved in the host defense mechanism that inactivates both endogenous and exogenous proteases, including trypsin, thrombin and collagenase. Even though A2M is produced predominantly by the liver, it may also be expressed in the reproductive tract, heart, and brain, and may have important roles in many physiological processes and medical illnesses including Alzheimer's disease.