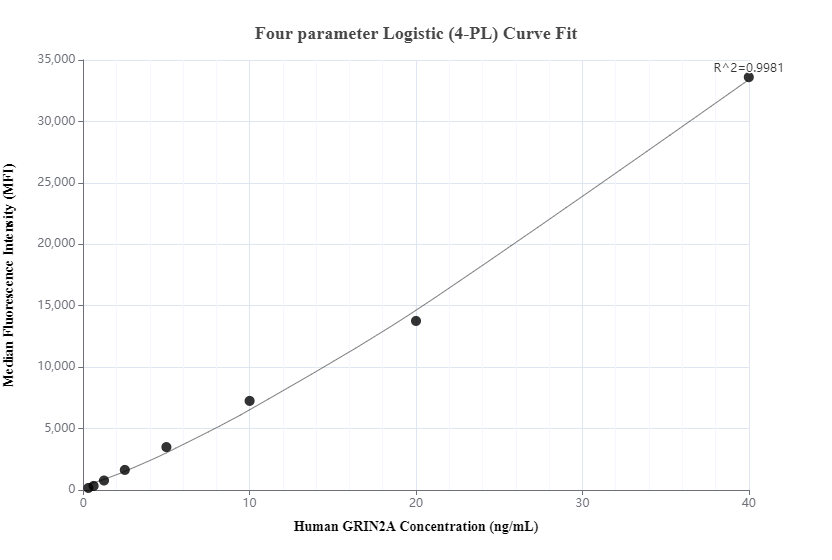
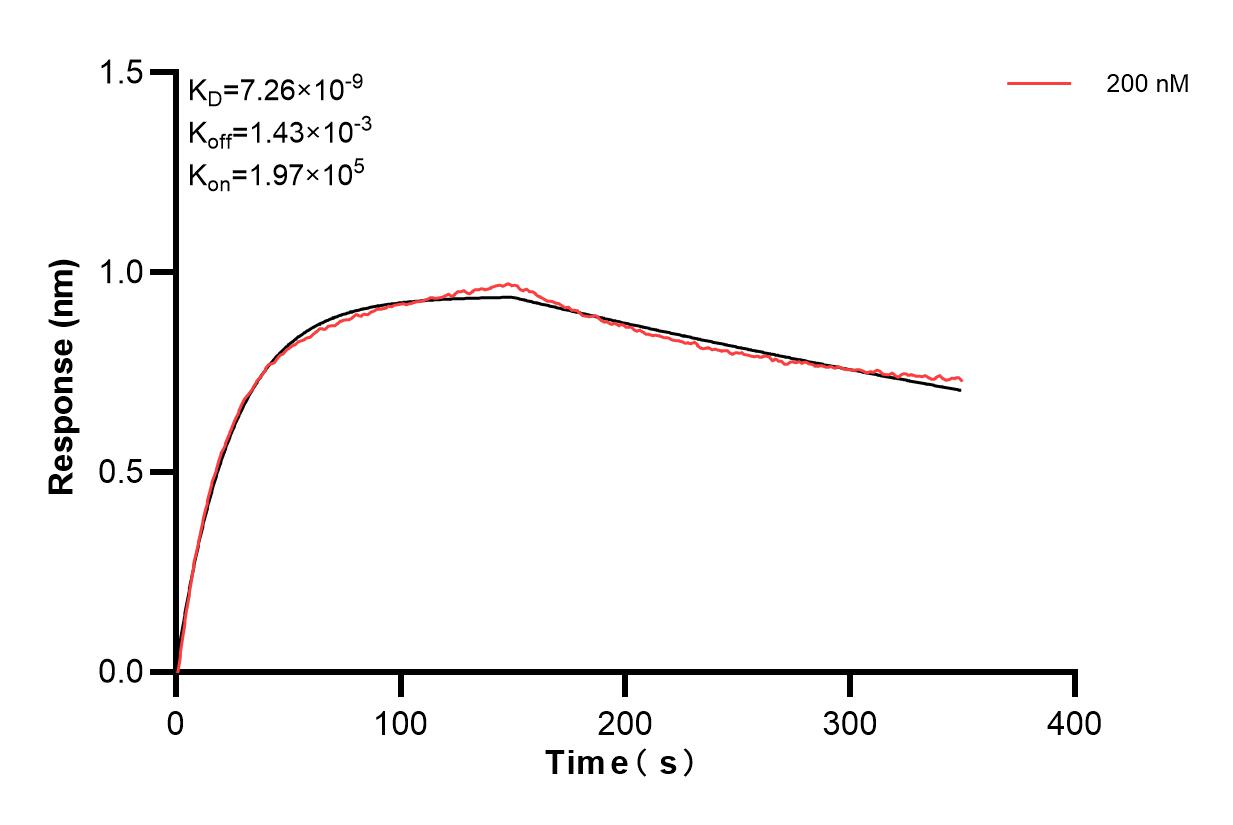
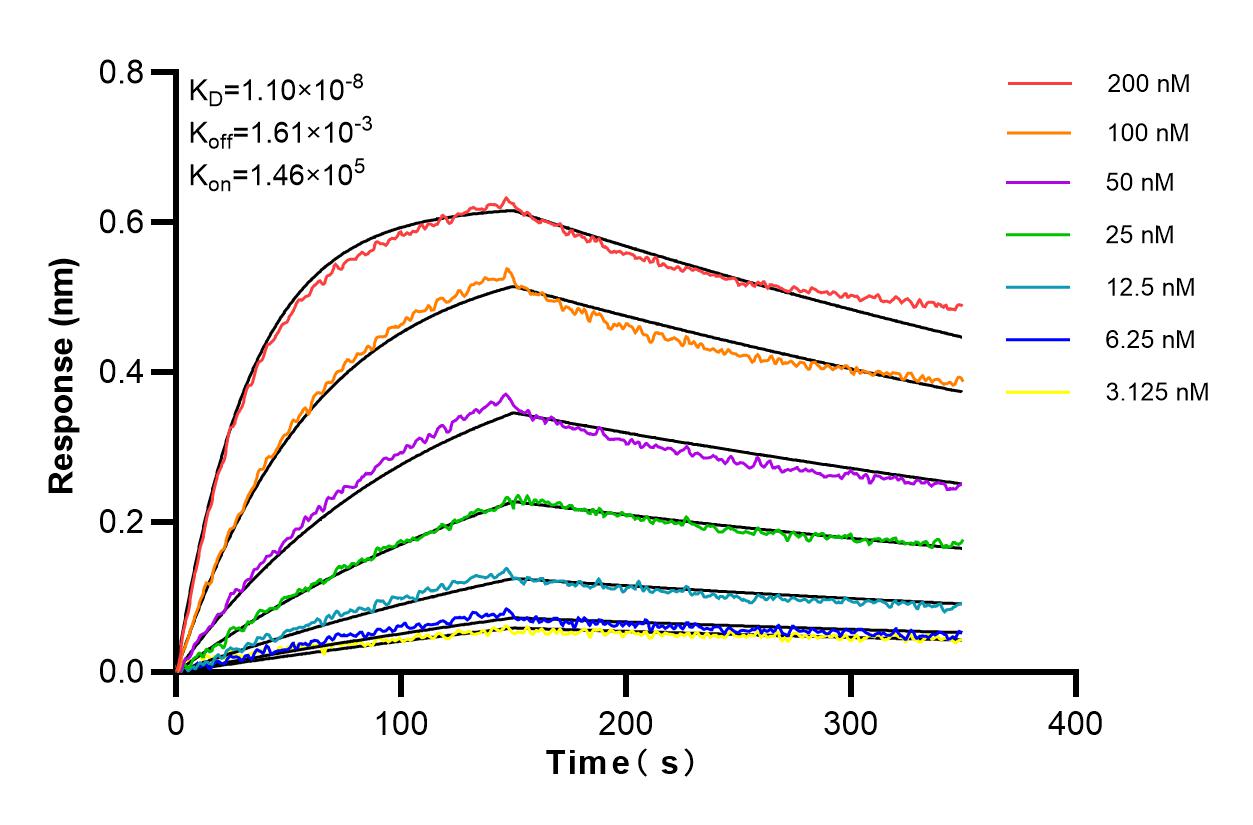
验证数据展示
产品信息
83465-2-PBS targets NMDAR2A/GRIN2A as part of a matched antibody pair:
MP00461-2: 83465-4-PBS capture and 83465-2-PBS detection (validated in Cytometric bead array)
Unconjugated rabbit recombinant monoclonal antibody in PBS only (BSA and azide free) storage buffer at a concentration of 1 mg/mL, ready for conjugation. Created using Proteintech’s proprietary in-house recombinant technology. Recombinant production enables unrivalled batch-to-batch consistency, easy scale-up, and future security of supply.
This conjugation ready format makes antibodies ideal for use in many applications including: ELISAs, multiplex assays requiring matched pairs, mass cytometry, and multiplex imaging applications.Antibody use should be optimized by the end user for each application and assay.
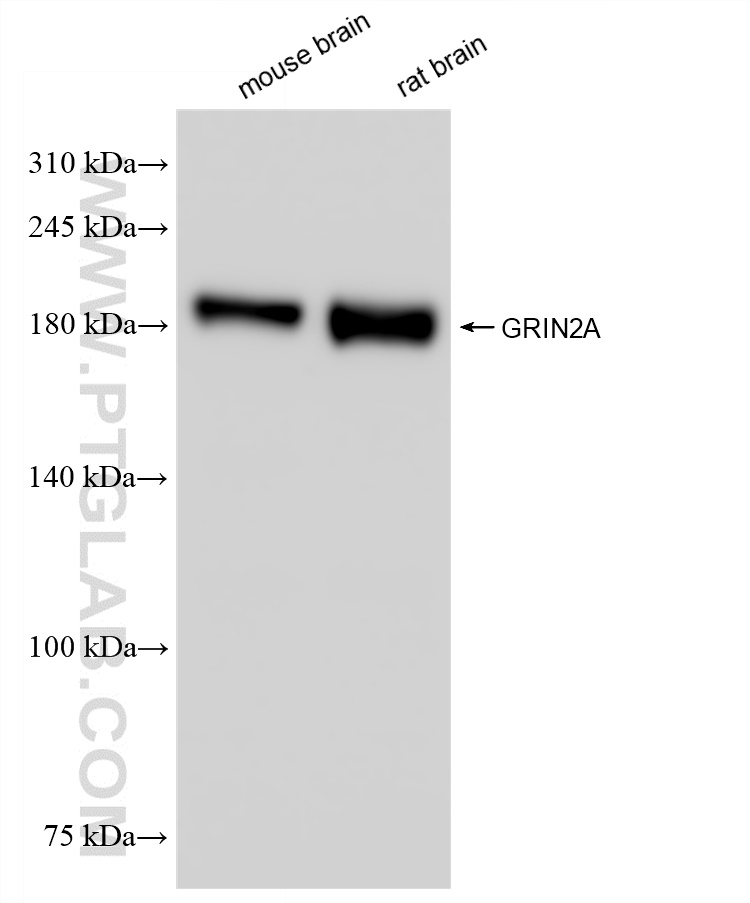
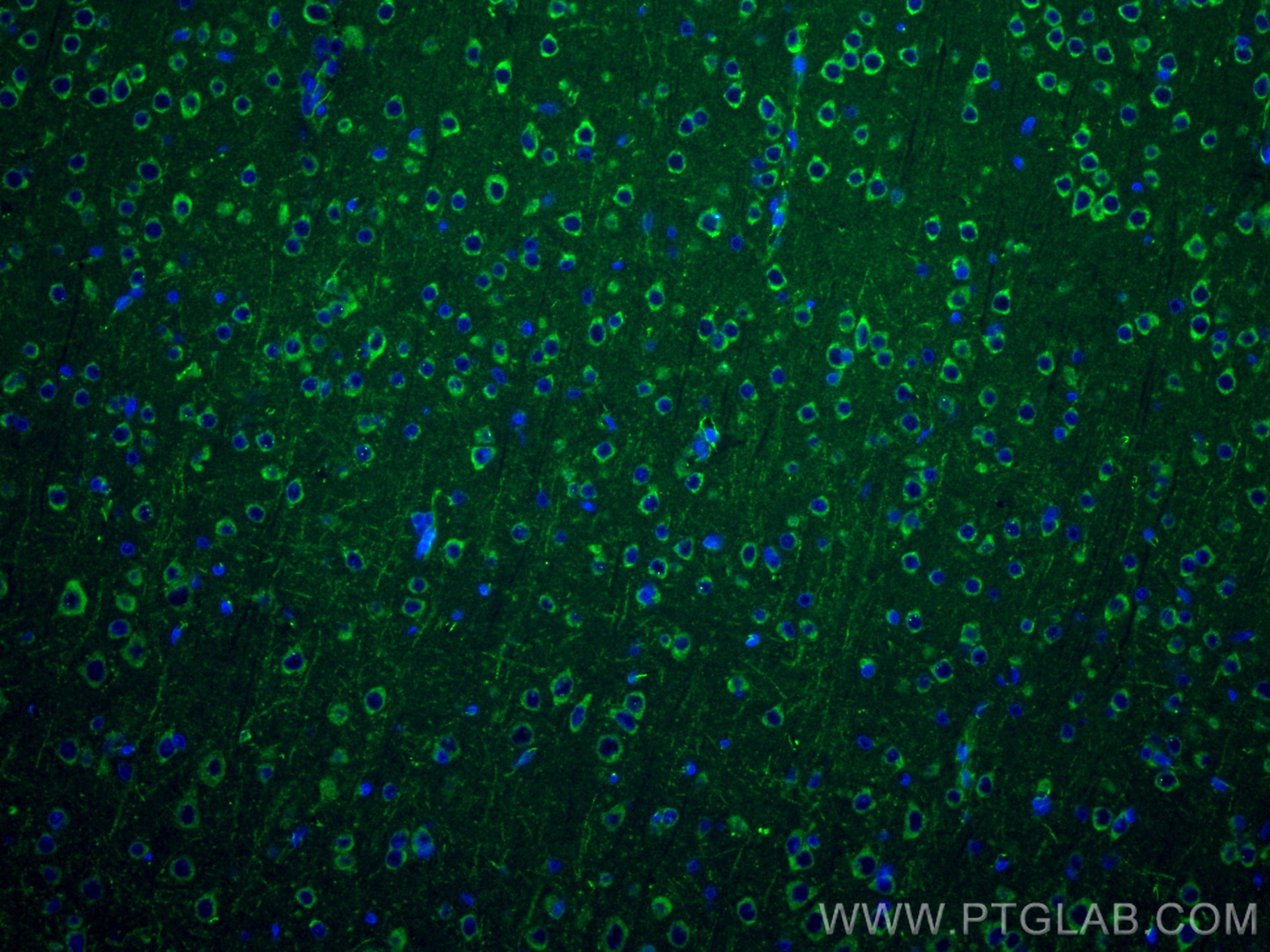
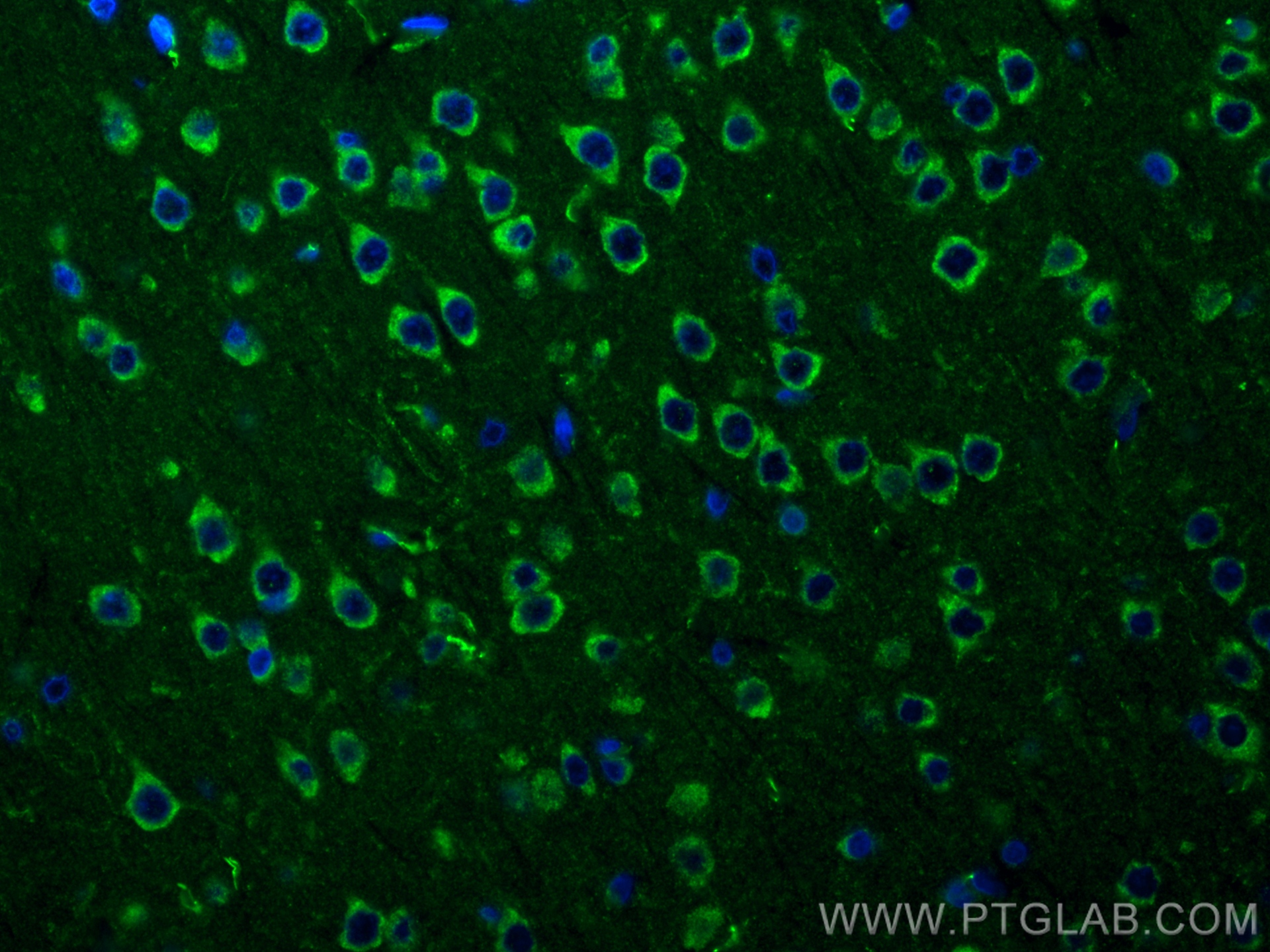
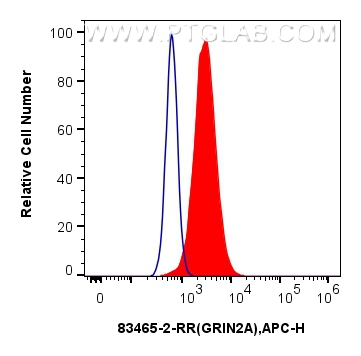
| 经测试应用 | WB, IF-P, FC (Intra), Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human, mouse, rat |
| 免疫原 | NMDAR2A/GRIN2A fusion protein Ag29101 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Recombinant |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 2A |
| 别名 | GRIN2A, NMDAR2A, hNR2A, Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2A, Glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit epsilon-1 |
| 计算分子量 | 165 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 160-180 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | NM_000833 |
| 基因名称 | GRIN2A |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2903 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q12879 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
GRIN2A (glutamate ionotropic receptor NMDA type subunit 2A), also known as NMDAR2A. And its molecular weight is 165 kDa. GRIN2A is located in cell projection, dendritic spine, cell membrane, synapse, postsynaptic cell membrae, cytolamic vesicle membrane, which is expressed in many tissues, highest expression in brain and heart. This gene encodes a member of the glutamate-gated ion channel protein family. The encoded protein is an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor subunit. NMDA receptors are both ligand-gated and voltage-dependent, and are involved in long-term potentiation, an activity-dependent increase in the efficiency of synaptic transmission thought to underlie certain kinds of memory and learning. These receptors are permeable to calcium ions, and activation results in a calcium influx into post-synaptic cells, which results in the activation of several signaling cascades. Disruption of this gene is associated with focal epilepsy and speech disorder with or without cognitive disability. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.