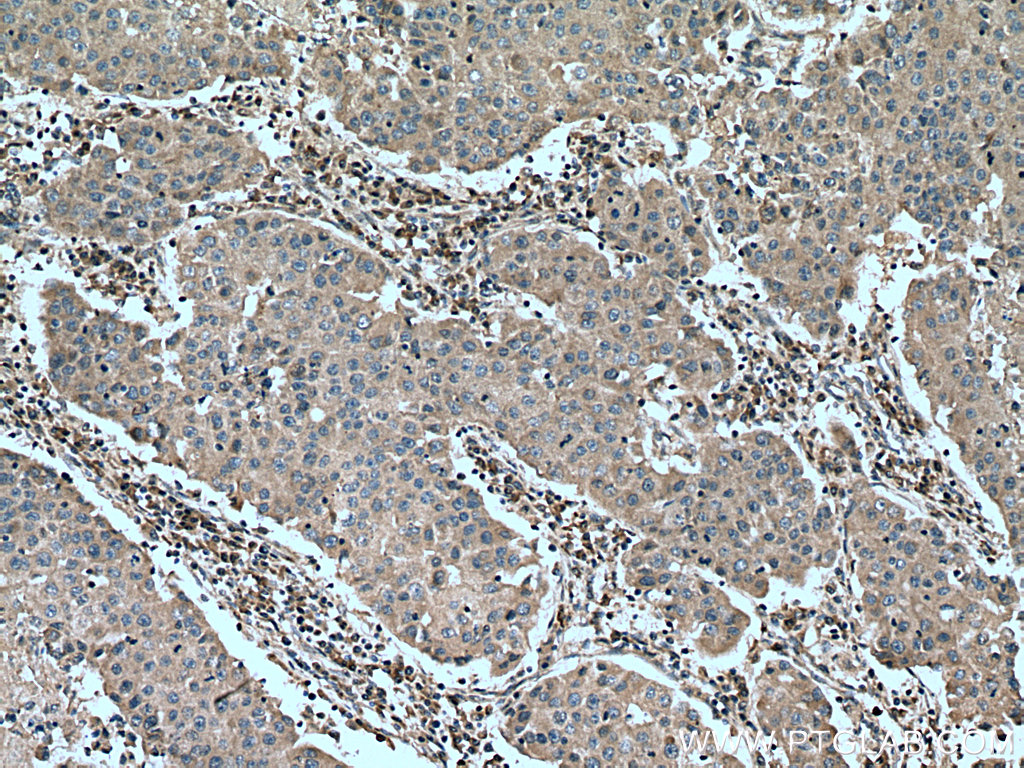
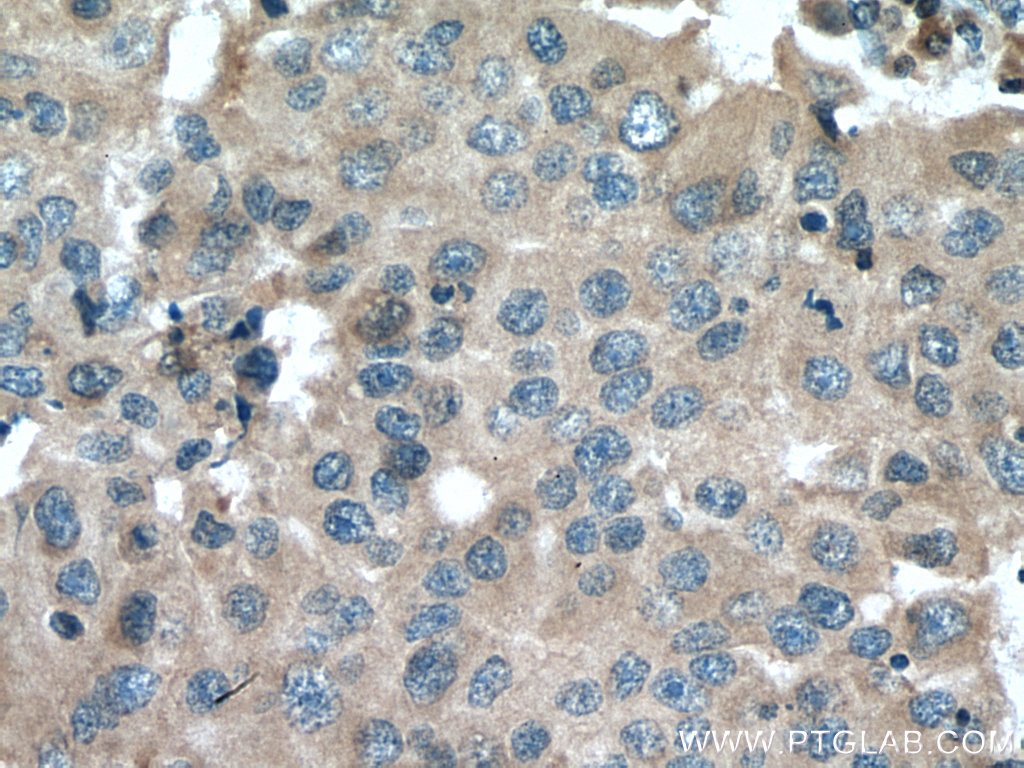
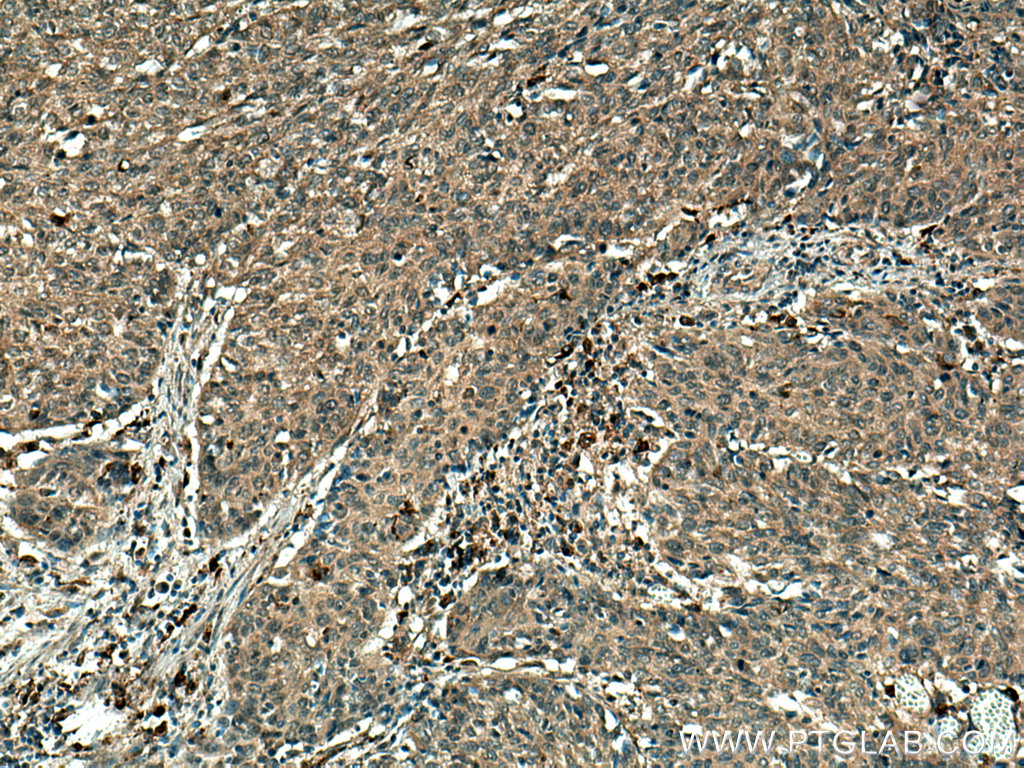
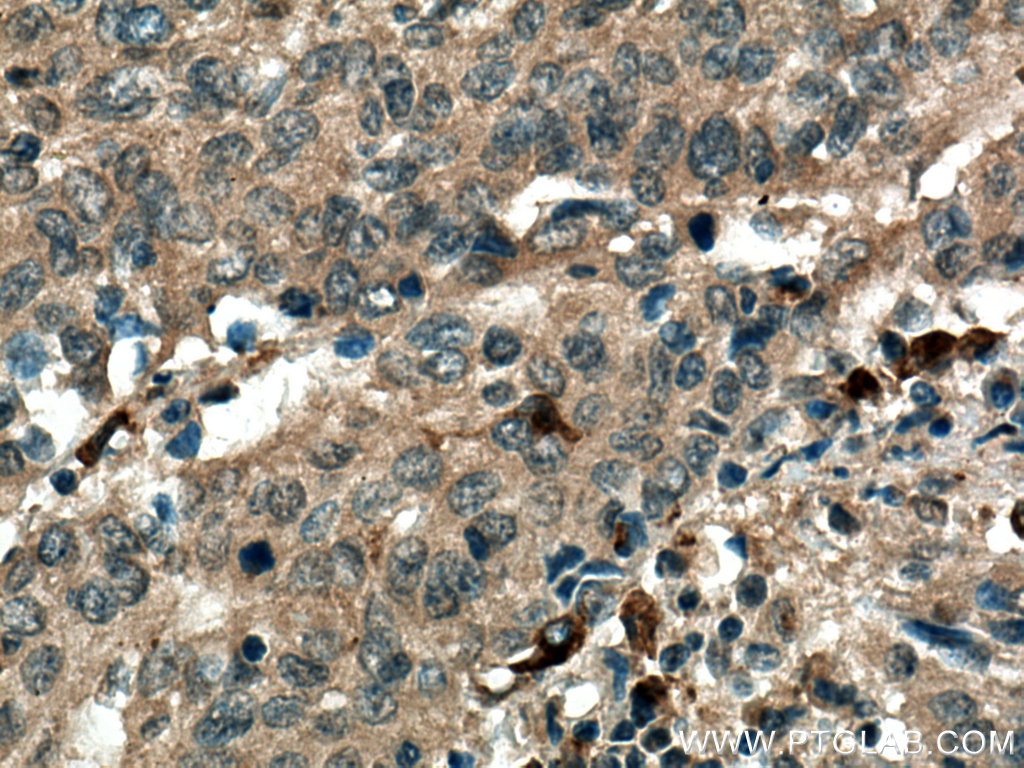
验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
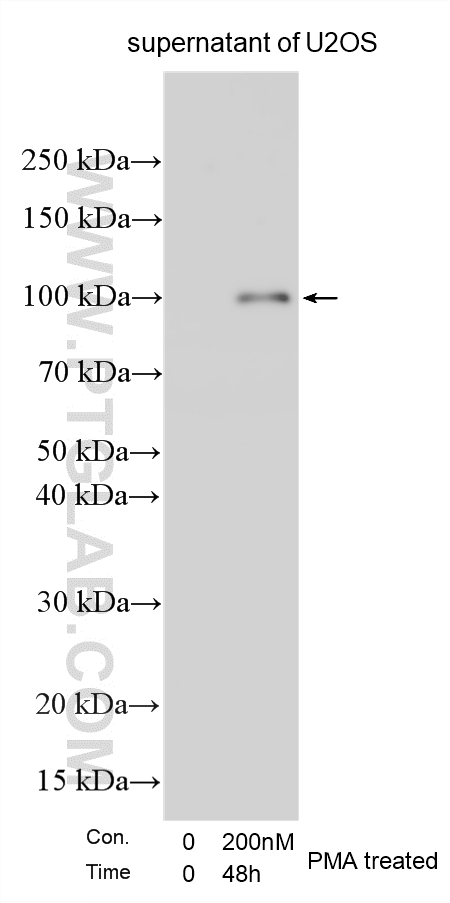
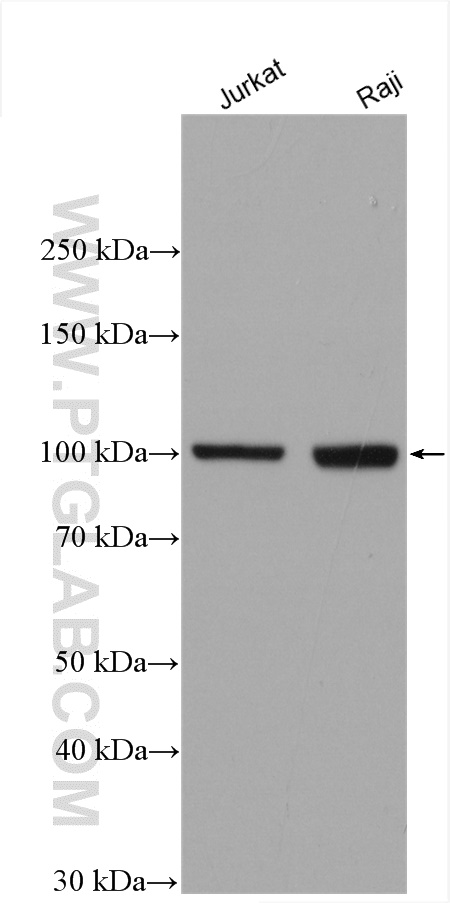
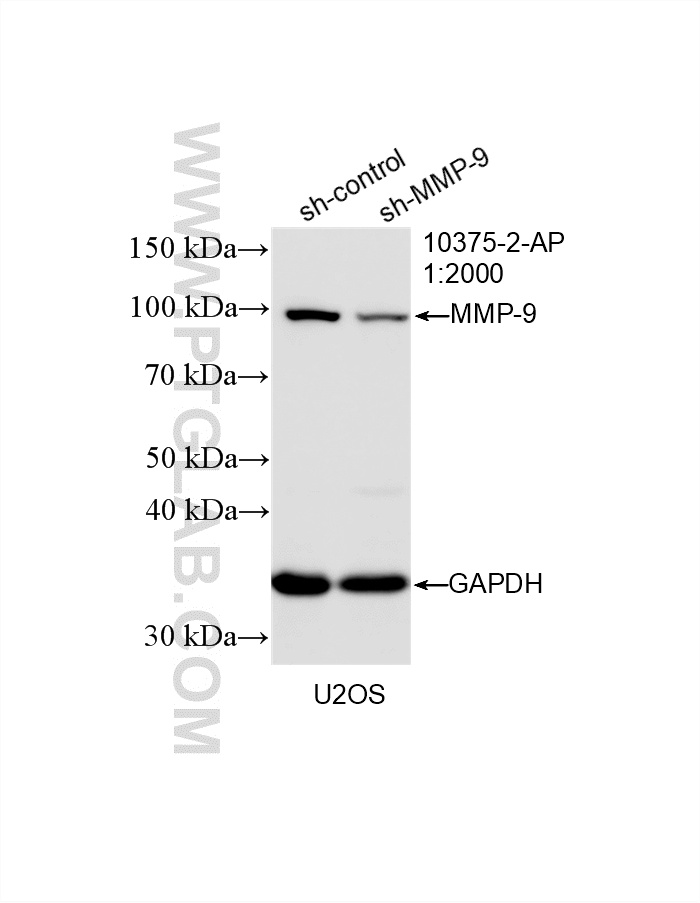
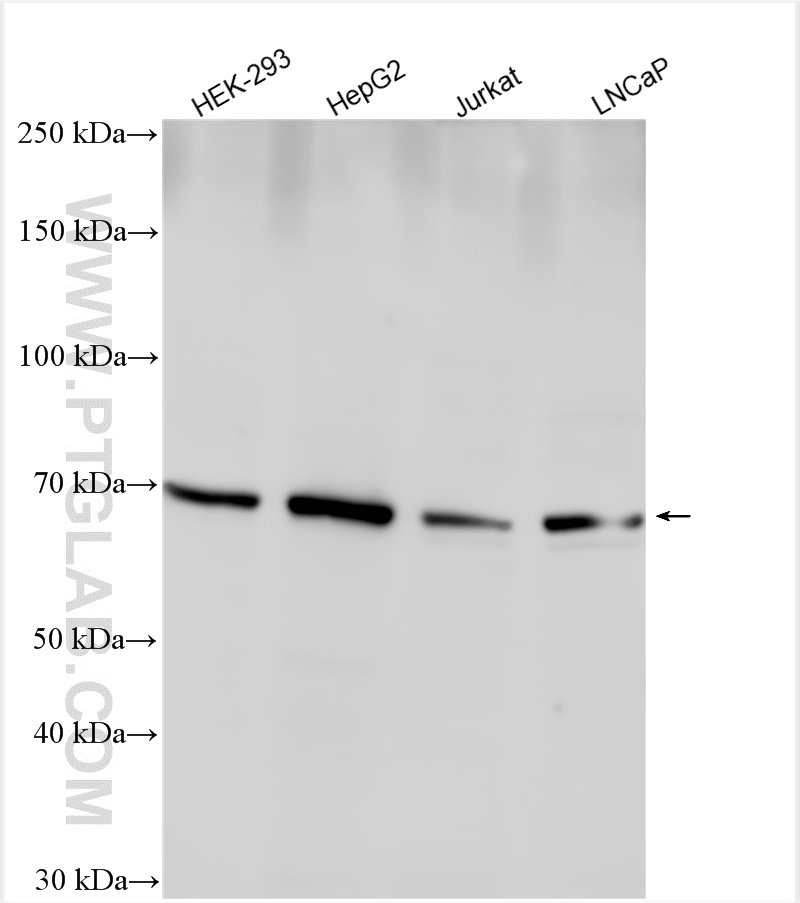
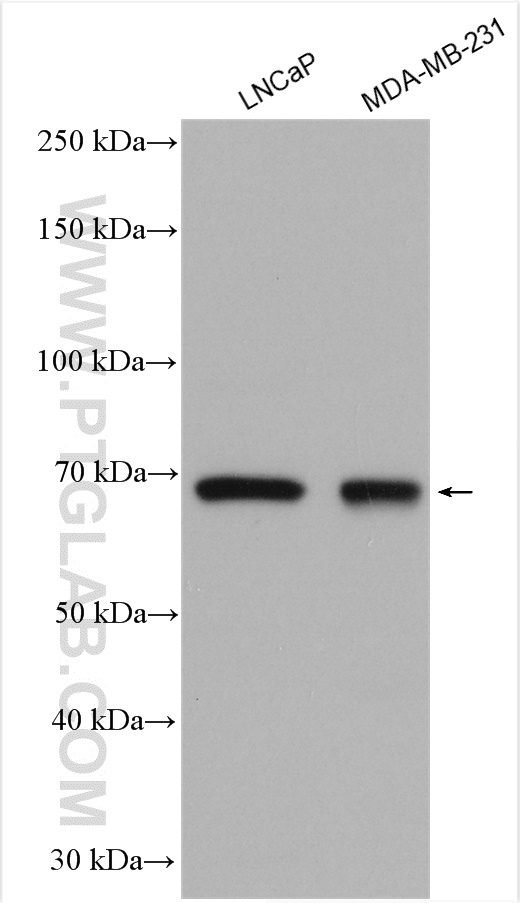
| Positive WB detected in | Jurkat cells, HEK-293 cells, LNCaP cells, U2OS cells, HepG2 cells, Raji cells, MDA-MB-231 cells |
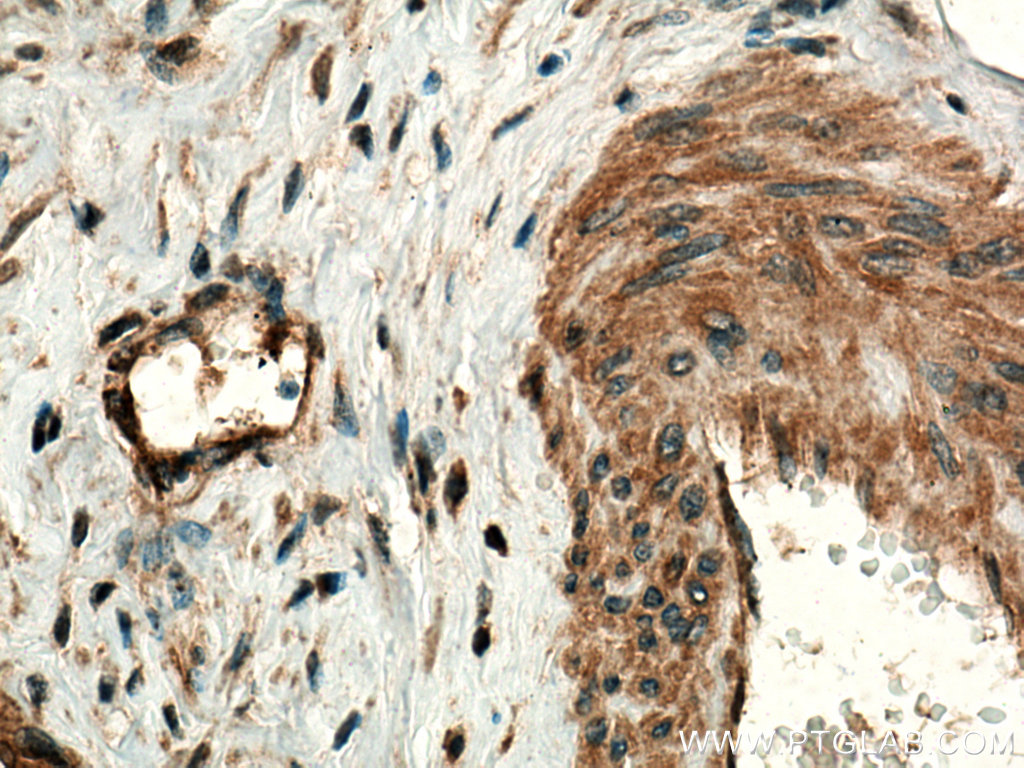
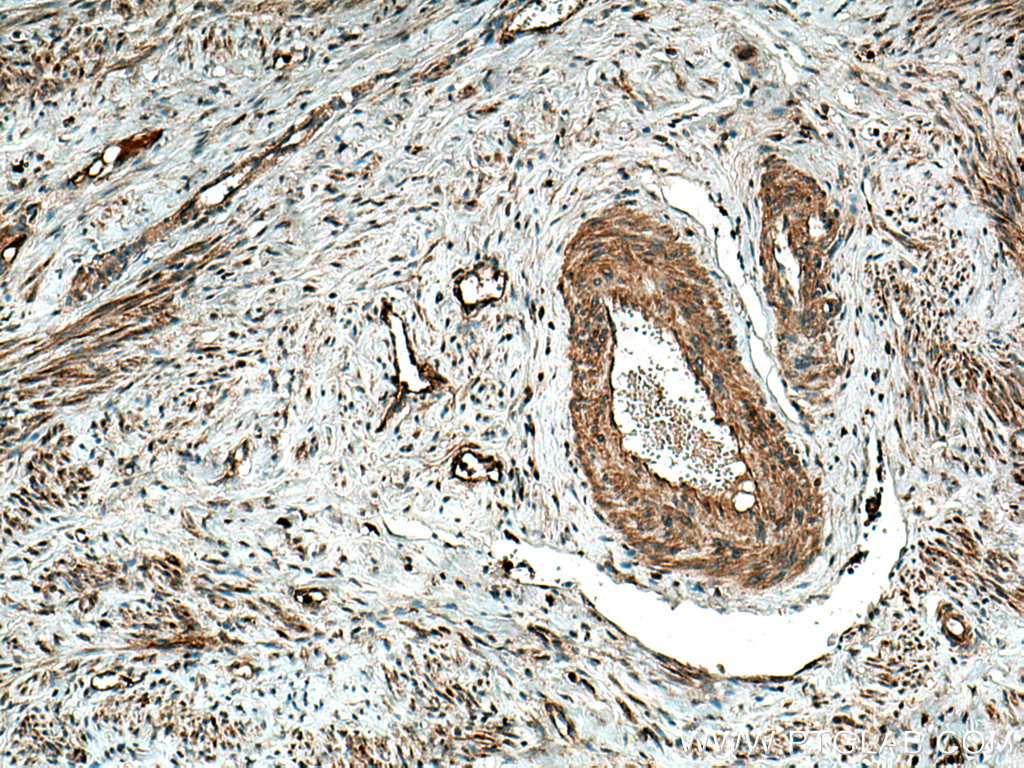
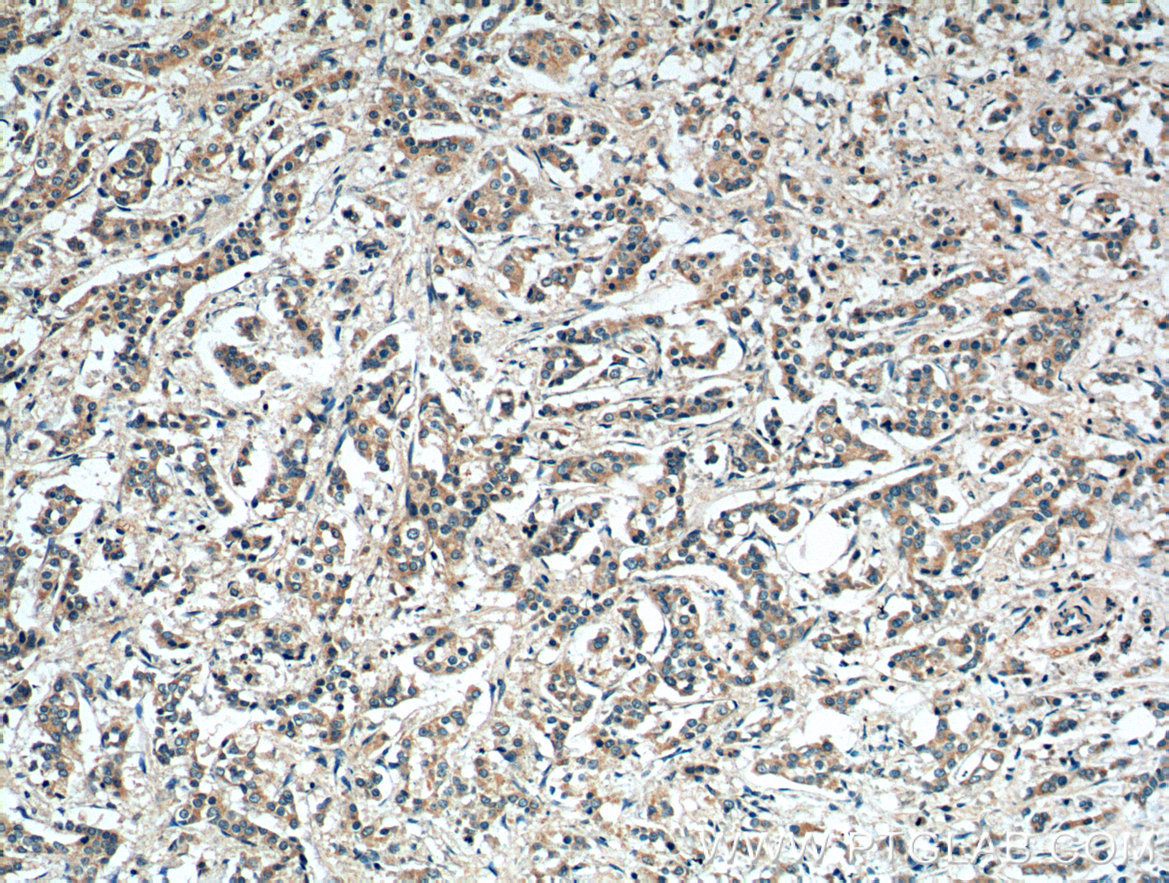
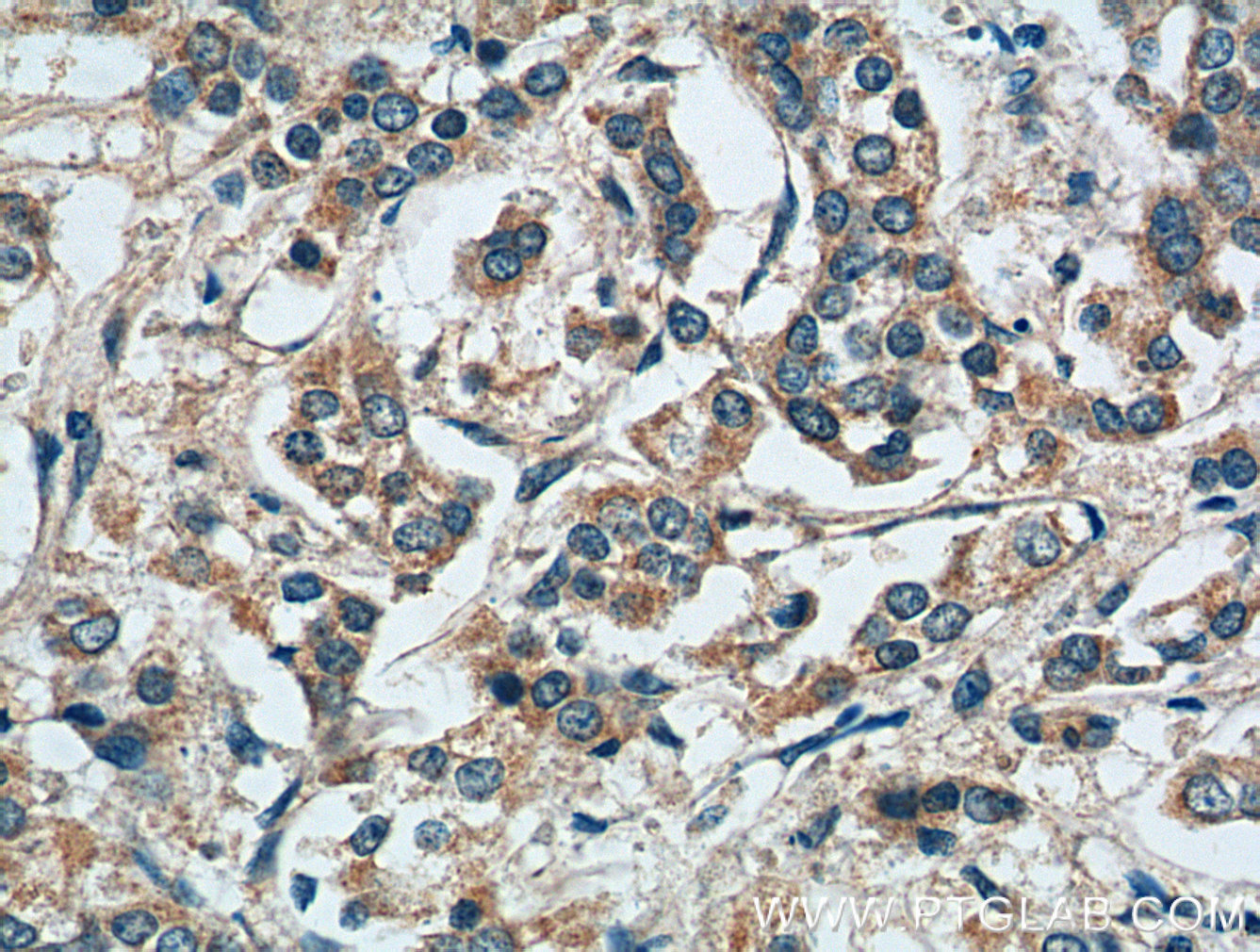
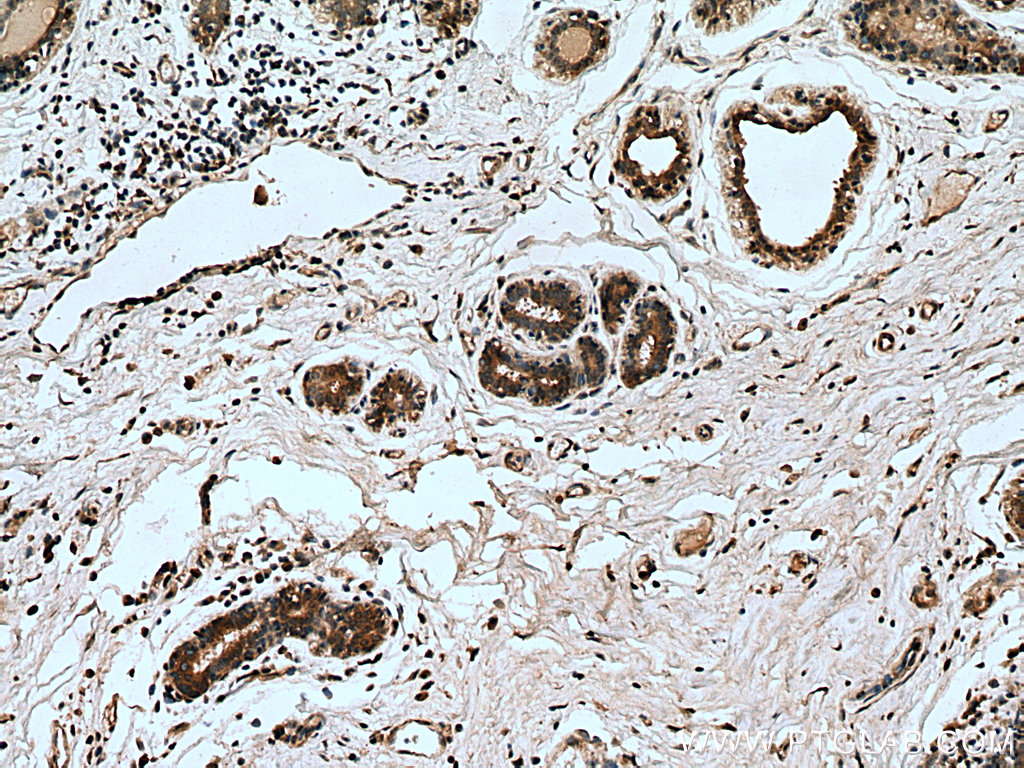
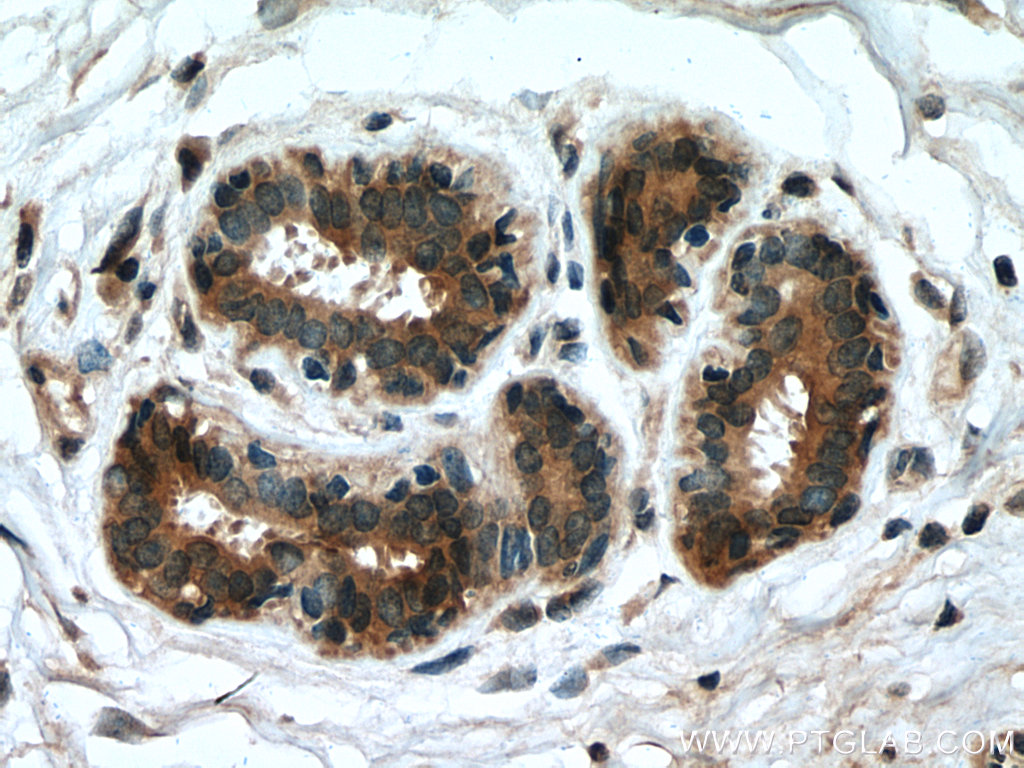
| Positive IHC detected in | human breast cancer tissue, human cervical cancer tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
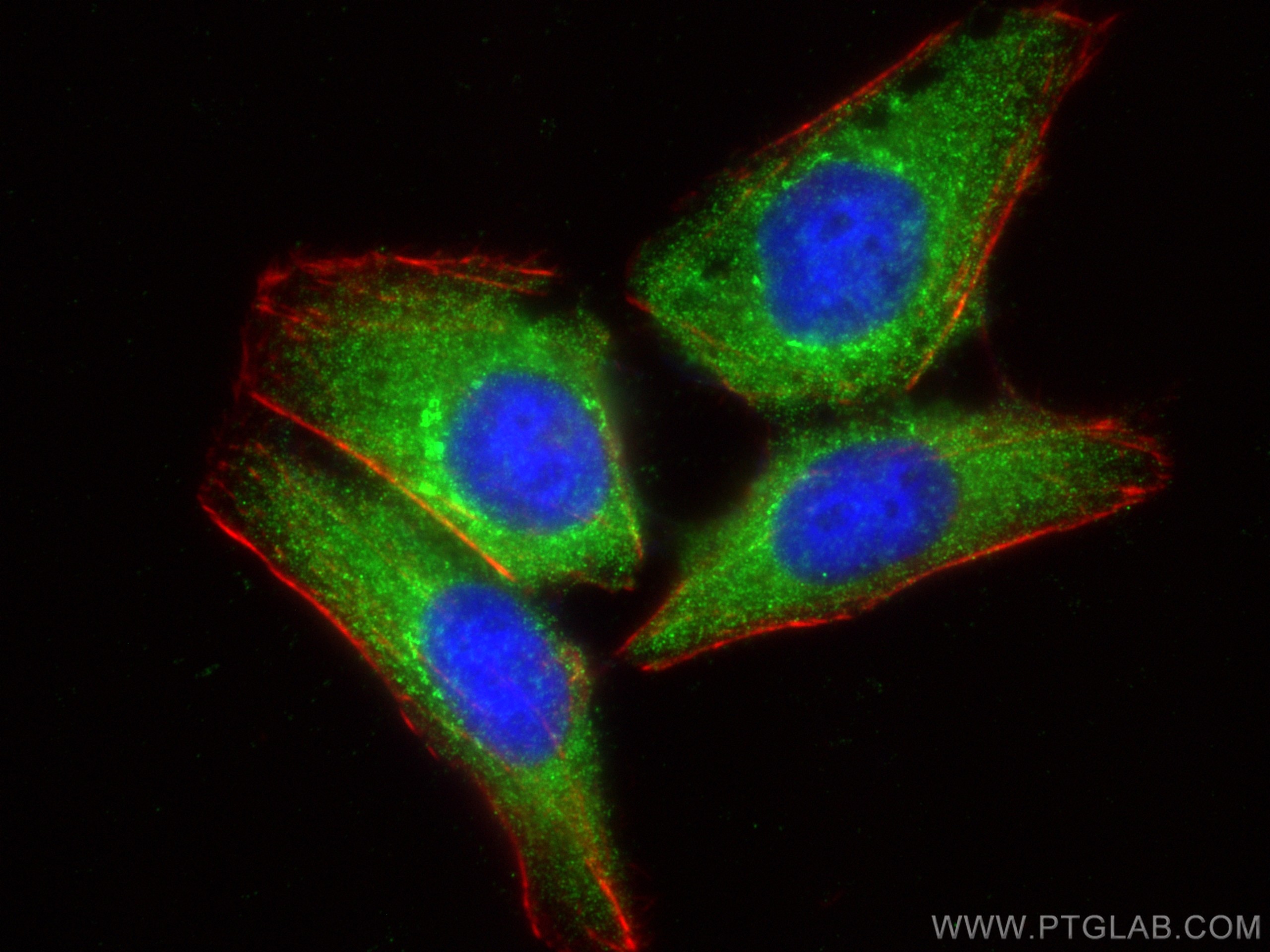
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HepG2 cells |
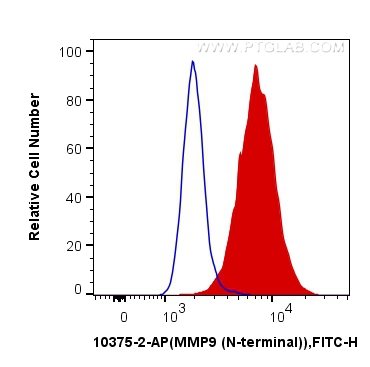
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | HeLa cells |
推荐稀释比
| 应用 | 推荐稀释比 |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:3000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.40 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
产品信息
10375-2-AP targets MMP-9 (N-terminal) in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), CoIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), ELISA Application Description |
| 文献引用应用 | WB, IHC, IF, CoIP, ELISA |
| 经测试反应性 | human |
| 文献引用反应性 | human, mouse, rat, pig, rabbit, bovine, hamster, fish |
| 免疫原 |
CatNo: Ag0552 Product name: Recombinant human MMP9 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-100 aa of BC006093 Sequence: MSLWQPLVLVLLVLGCCFAAPRQRQSTLVLFPGDLRTNLTDRQLAEEYLYRYGYTRVAEMRGESKSLGPALLLLQKQLSLPETGELDSATLKAMRTPRCG 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Polyclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | matrix metallopeptidase 9 (gelatinase B, 92kDa gelatinase, 92kDa type IV collagenase) |
| 别名 | MMP9 (N-terminal), MMP9, 67 kDa matrix metalloproteinase-9, 82 kDa matrix metalloproteinase-9, CLG4B |
| 计算分子量 | 707 aa, 78 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 92 kDa, 67 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC006093 |
| 基因名称 | MMP-9 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4318 |
| RRID | AB_10897178 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P14780 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
背景介绍
Proteins of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, tissue remodeling, and disease processes, such as arthritis or metastasis. Most MMP's are secreted as inactive proproteins which are activated when cleaved by extracellular proteinases. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (gelatinase B, 92 kDa gelatinase, 92 kDa type IV collagenase) (MMP9, synonyms: GELB, CLG4B) degrades collagens type IV and V. Studies in rhesus monkeys suggest that MMP9 is involved in IL-8-induced mobilization hematopoietic progenitor cells from bone marrow, and murine studies suggest a role in tumor-associated tissue remodeling. The pro-MMP9 is 92 kDa, and it can be detected a processed form of 68 kDa. This protein can exist as a dimer of 180 kDa (PMID:7492685).
实验方案
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for MMP-9 (N-terminal) antibody 10375-2-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for MMP-9 (N-terminal) antibody 10375-2-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for MMP-9 (N-terminal) antibody 10375-2-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for MMP-9 (N-terminal) antibody 10375-2-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
发表文章
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Gastroenterology Regulator of Calcineurin 1 Gene Isoform 4, Downregulated in Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Prevents Proliferation, Migration, and Invasive Activity of Cancer Cells and Growth of Orthotopic Tumors by Inhibiting Nuclear Translocation of NFAT1. | ||
Cell Host Microbe Gut microbiome dysbiosis contributes to abdominal aortic aneurysm by promoting neutrophil extracellular trap formation | ||
Mol Cancer CircEZH2/miR-133b/IGF2BP2 aggravates colorectal cancer progression via enhancing the stability of m6A-modified CREB1 mRNA. | ||
Adv Sci (Weinh) Bone Marrow-Derived GCA+ Immune Cells Drive Alzheimer's Disease Progression | ||
J Pineal Res Melatonin modulates metabolic remodeling in HNSCC by suppressing MTHFD1L-formate axis. | ||
Acta Pharm Sin B Engineering cannabidiol synergistic carbon monoxide nanocomplexes to enhance cancer therapy via excessive autophagy |