验证数据展示
产品信息
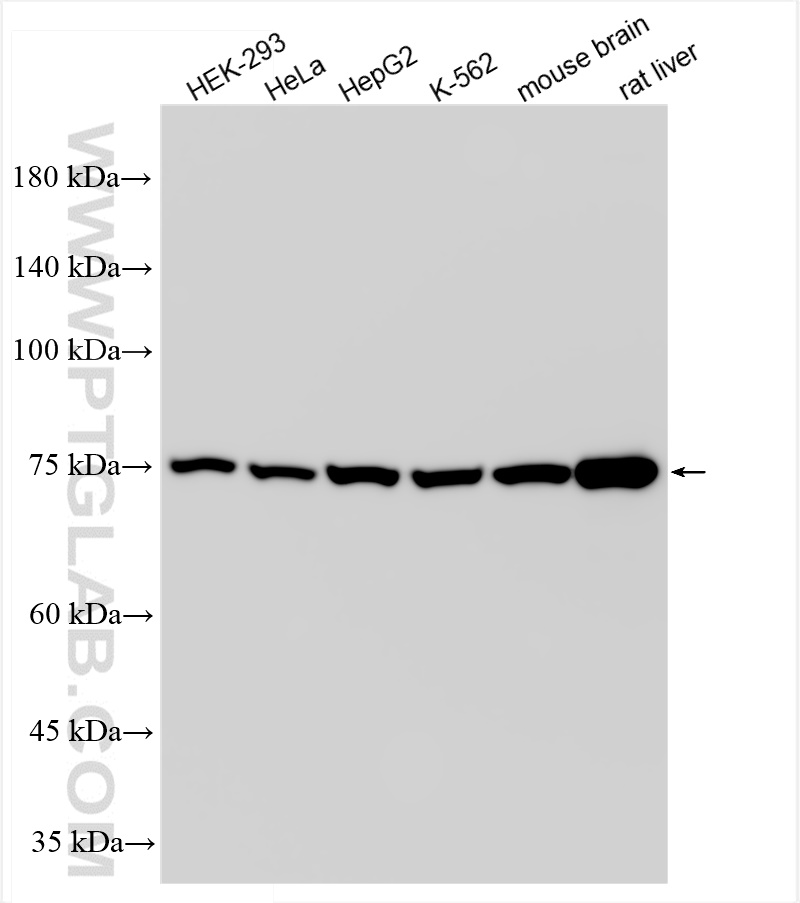
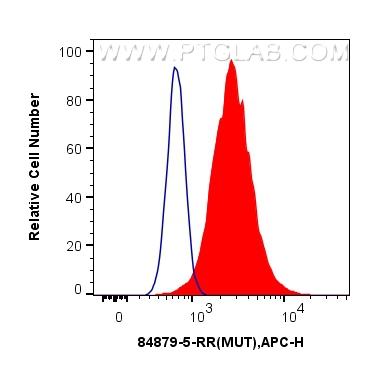
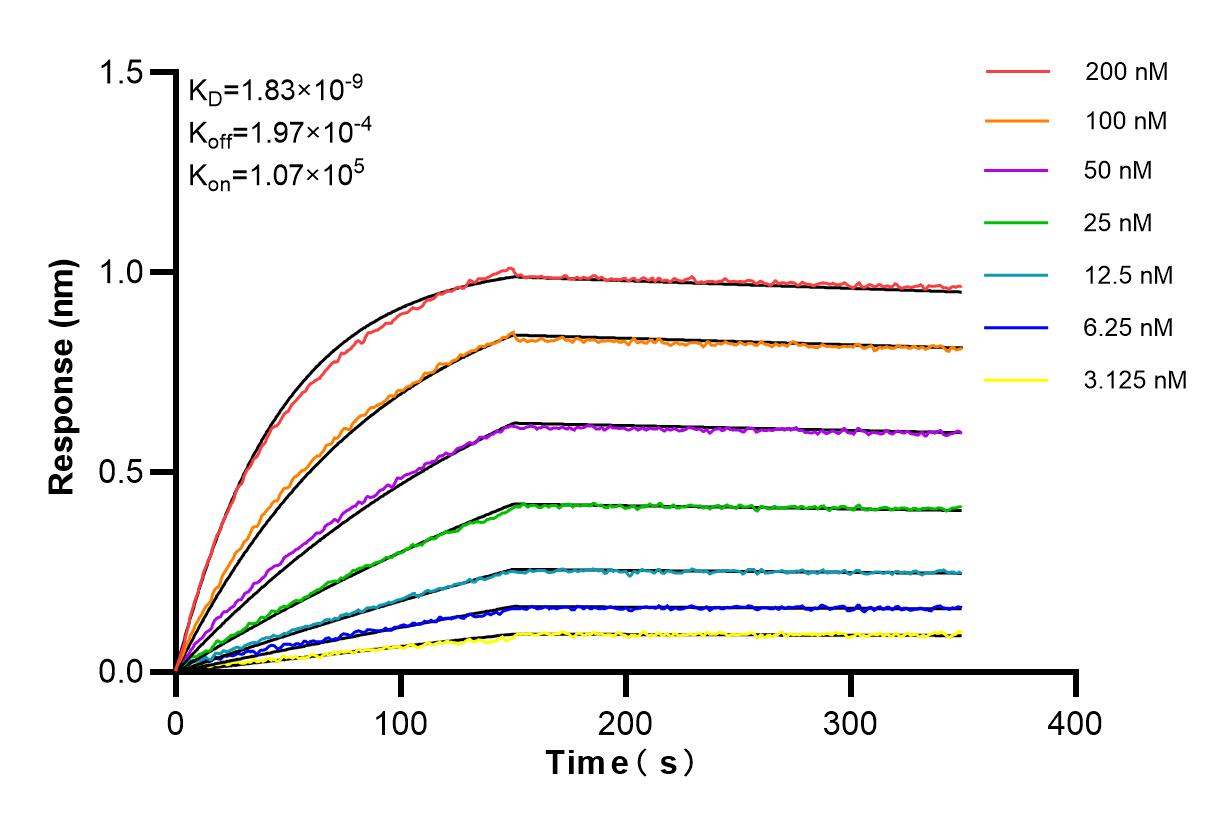
84879-5-PBS targets Methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase/MUT in WB, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human, mouse, rat |
| 免疫原 | Methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase/MUT fusion protein Ag10523 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Recombinant |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase |
| 别名 | MUT, Methylmalonyl-CoA isomerase, Methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase, Methylmalonyl CoA isomerase, MCM |
| 计算分子量 | 750 aa, 83 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 78 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC016282 |
| 基因名称 | MUT |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4594 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purfication |
| UNIPROT ID | P22033 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
Methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase (MUT) is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the metabolism of certain amino acids and fatty acids. Mutations in the MUT gene can lead to methylmalonic acidemia, a metabolic disorder characterized by the accumulation of toxic compounds such as methylmalonyl-CoA and propionyl-CoA. This condition can cause severe health issues including developmental delays, metabolic acidosis, and neurological problems. MUT is essential for maintaining normal metabolic processes and its dysfunction can have significant health implications, highlighting its importance in both basic metabolism and clinical medicine.