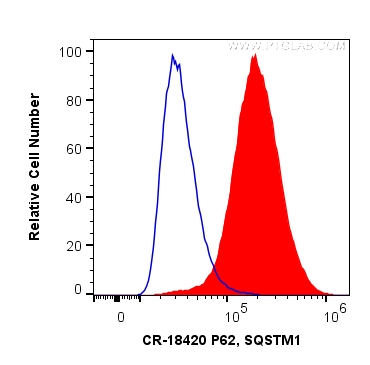
验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | HeLa cells |
推荐稀释比
| 应用 | 推荐稀释比 |
|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.20 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
产品信息
CR-18420 targets P62/SQSTM1 in FC (Intra) applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| 经测试应用 | FC (Intra) Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human |
| 免疫原 |
CatNo: Ag13131 Product name: Recombinant human P62;SQSTM1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-440 aa of BC017222 Sequence: MASLTVKAYLLGKEDAAREIRRFSFCCSPEPEAEAEAAAGPGPCERLLSRVAALFPALRPGGFQAHYRDEDGDLVAFSSDEELTMAMSYVKDDIFRIYIKEKKECRRDHRPPCAQEAPRNMVHPNVICDGCNGPVVGTRYKCSVCPDYDLCSVCEGKGLHRGHTKLAFPSPFGHLSEGFSHSRWLRKVKHGHFGWPGWEMGPPGNWSPRPPRAGEARPGPTAESASGPSEDPSVNFLKNVGESVAAALSPLGIEVDIDVEHGGKRSRLTPVSPESSSTEEKSSSQPSSCCSDPSKPGGNVEGATQSLAEQMRKIALESEGRPEEQMESDNCSGGDDDWTHLSSKEVDPSTGELQSLQMPESEGPSSLDPSQEGPTGLKEAALYPHLPPEADPRLIESLSQMLSMGFSDEGGWLTRLLQTKNYDIGAALDTIQYSKHPPPL 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Polyclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | sequestosome 1 |
| 别名 | P62,SQSTM1, P62, SQSTM1, EBI3-associated protein of 60 kDa, Phosphotyrosine-independent ligand for the Lck SH2 domain of 62 kDa |
| 计算分子量 | 48 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 62 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC017222 |
| 基因名称 | P62/SQSTM1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 8878 |
| RRID | AB_2934338 |
| 偶联类型 | Cardinal Red™ Fluorescent Dye |
| 最大激发/发射波长 | 592 nm / 611 nm |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q13501 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
背景介绍
Background
P62 (ubiquitin-binding protein P62), also known as Sequestosome-1, is a multifunctional adaptor protein most widely known for its role as an autophagosome cargo protein (PMID: 8551575). P62 via specific interactions with polyubiquitylated target proteins induces their selective autophagy (PMID: 17580304). It also plays an important role in the regulation of the NFkB signaling pathway, senescence, cell differentiation, apoptosis, and immune responses (PMID: 26404812).
What is the molecular weight of P62?
The observed molecular weight of the protein can vary from as low as 8 kDa (for the smallest isoforms) to 48 kDa.
What is the subcellular localization of P62?
P62 is mainly localized in the cytoplasm; however, upon autophagy induction, e.g., via starvation or selective inhibitor treatment, it localizes in vesicular structures - autophagosomes.
What is the tissue specificity of P62?
It is ubiquitously expressed in various tissues.
What is the function of P62 in the regulation of cell death and autophagy?
It is a selective autophagy receptor that forms a bridge between polyubiquitylated cargo (via its UBA domains) and an autophagy modifier such as LC3 (via LIR domains) (PMIDs: 16286508, 20168092, 24128730, 28404643, 22622177). The process of selective autophagy is tightly regulated at many levels, including the posttranslational modifications (PTMs) of various proteins in the cascade, P62 among others (PMID: 29233872). P62 is involved in the regulation of cell death induction in response to various stimuli, e.g., via activation of caspase-8 at the autophagosome membrane (PMID: 29480462). In addition, P62 is degraded during the autophagic process, which makes its intracellular level a marker for autophagy progression.
What is P62's involvement in disease?
Mutations in P62 have been associated with the following diseases: sporadic and familial Paget's disease of bone, neurodegenerative diseases, diabetes, and obesity (PMID: 29480462). A growing number of reports suggest the implication of P62 in the induction of multiple cellular oncogenic transformations. Indeed, increased levels of P62 have been linked to tumor formation, cancer promotion, and resistance to therapy (PMID: 29738493). Moreover, P62 is an unfavorable prognostic marker in liver cancer.
实验方案
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for Cardinal Red™ P62/SQSTM1 antibody CR-18420 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |