验证数据展示
产品信息
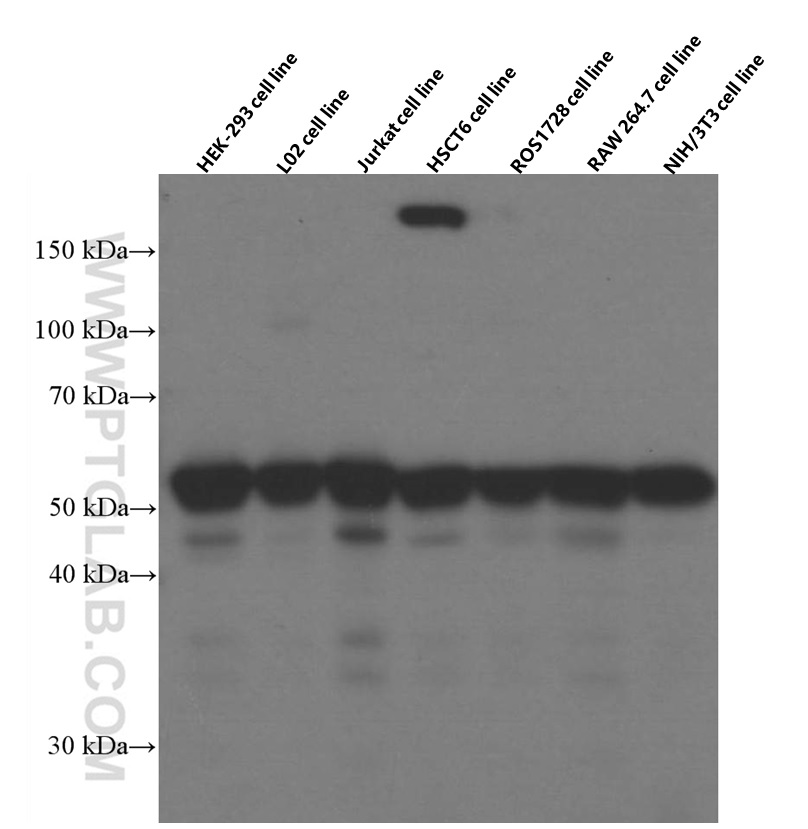
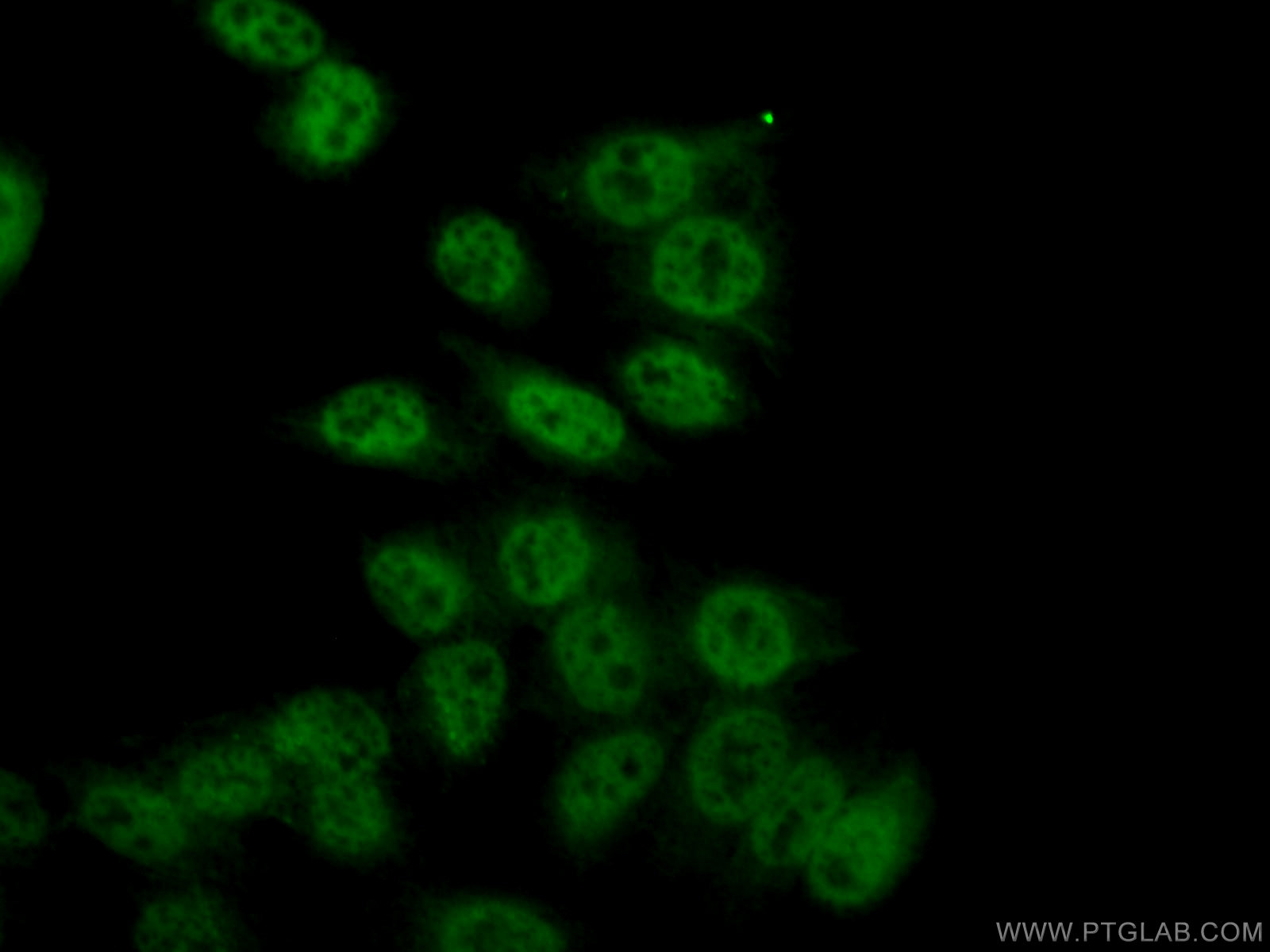
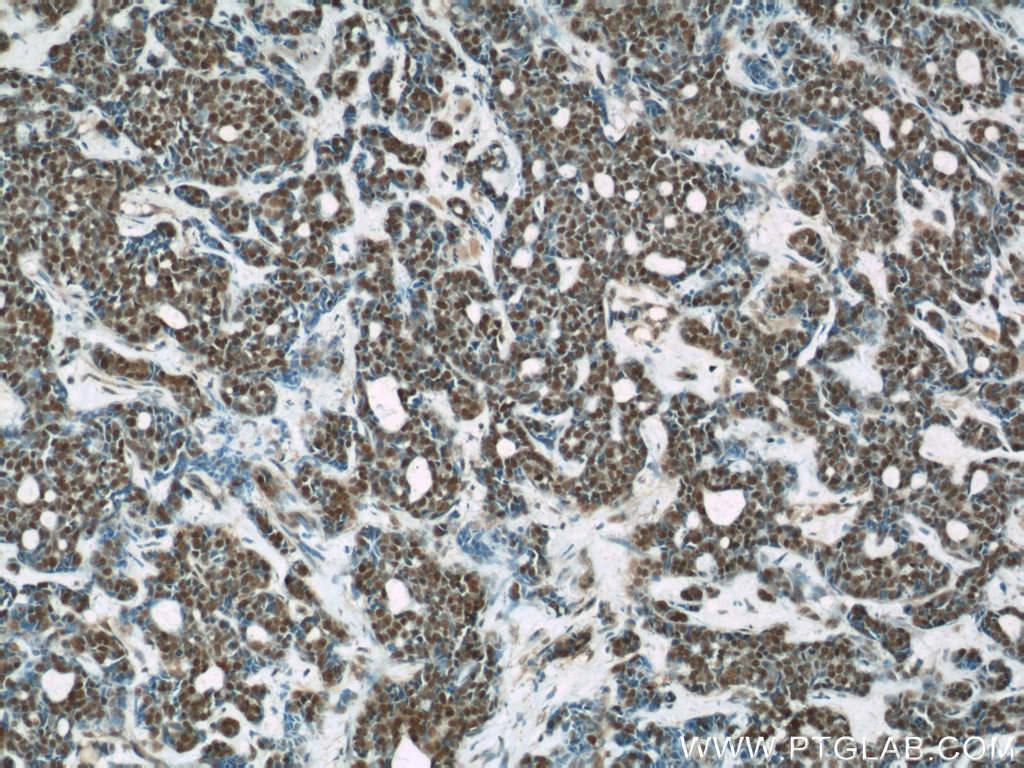
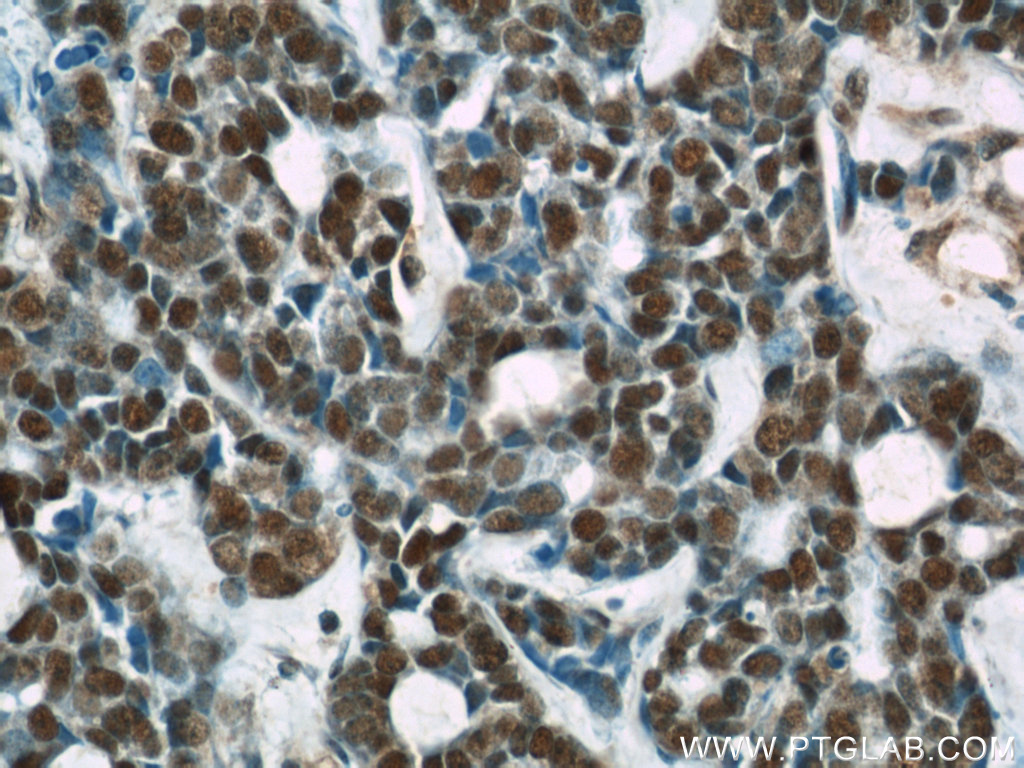
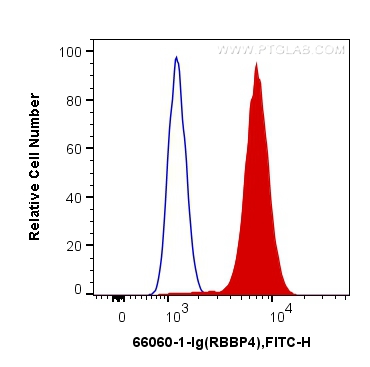
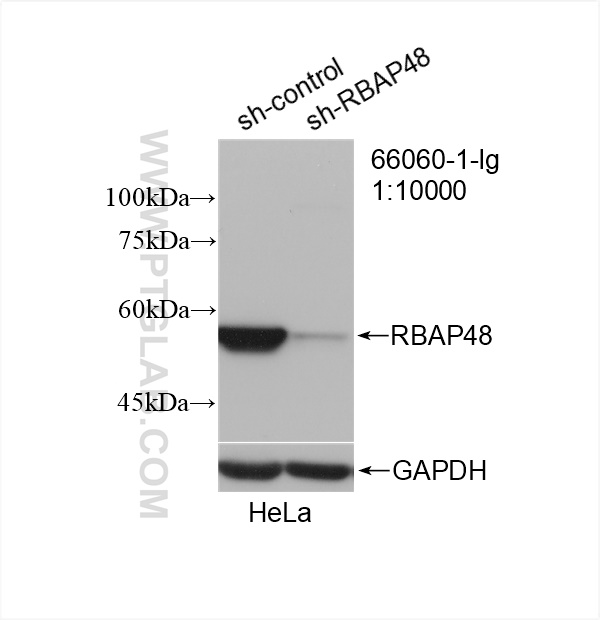
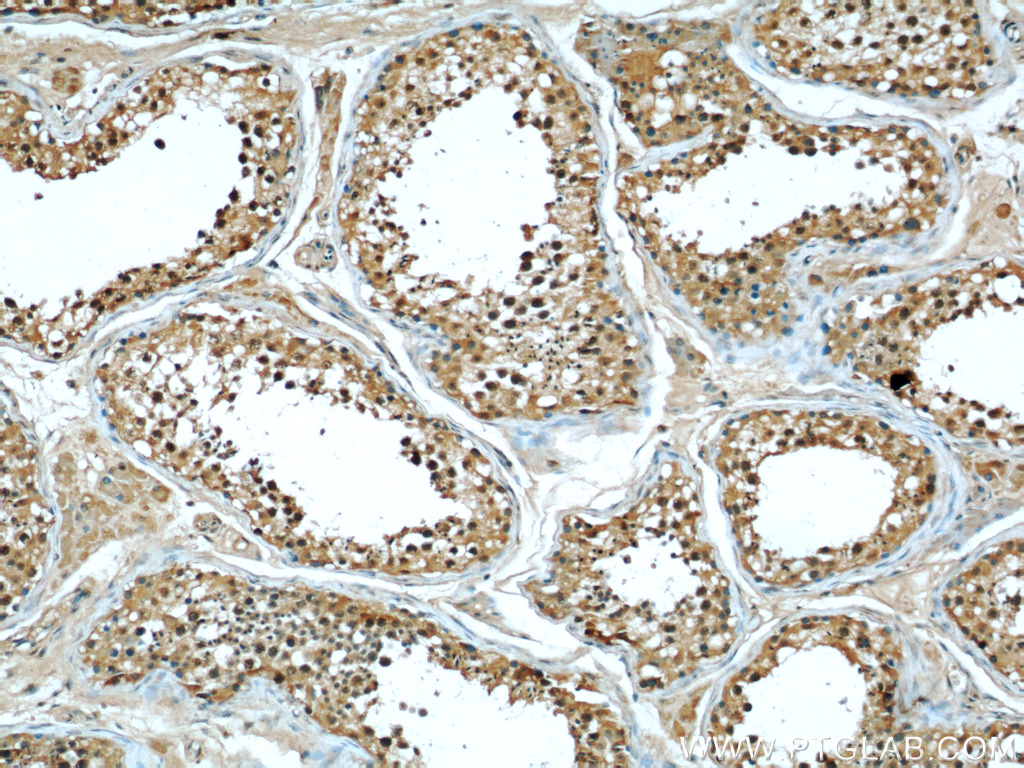
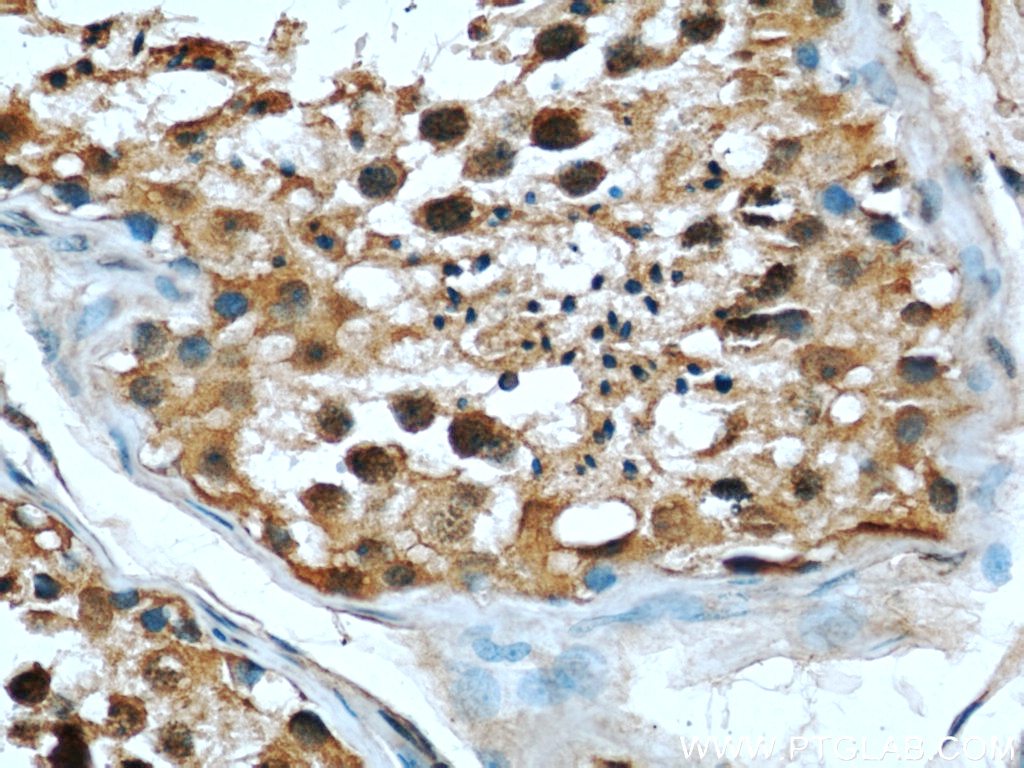
66060-1-PBS targets RBAP48 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with rat, mouse, human samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | rat, mouse, human |
| 免疫原 | RBAP48 fusion protein Ag6196 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Mouse / IgG2b |
| 抗体类别 | Monoclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | retinoblastoma binding protein 4 |
| 别名 | RBBP4, Nucleosome-remodeling factor subunit RBAP48, Histone-binding protein RBBP4, CAF-I p48, CAF-I 48 kDa subunit |
| 计算分子量 | 48 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 53 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC053904 |
| 基因名称 | RBBP4 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 5928 |
| RRID | AB_11064731 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q09028 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
Histone-binding protein RBBP4 (also known as RbAp48, or NURF55) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBBP4 gene. This gene encodes a ubiquitously expressed nuclear protein that belongs to a highly conserved subfamily of WD-repeat proteins. It is present in protein complexes involved in histone acetylation and chromatin assembly. It is part of the Mi-2/NuRD complex complex that has been implicated in chromatin remodeling and transcriptional repression associated with histone deacetylation. This encoded protein is also part of corepressor complexes, which is an integral component of transcriptional silencing. It is found among several cellular proteins that bind directly to retinoblastoma protein to regulate cell proliferation. A decrease of RbAp48 in the dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus in the brain is suspected to be a main cause of memory loss in normal aging (PMID: 23986399).