Blood-Brain Barrier Research
The blood brain barrier (BBB) is the main barrier for CNS protection and helps maintain ionic homeostasis and brain nutrition. Whilst being protective, it is also a huge obstacle in delivering drugs or other treatment strategies to the brain. BBB dysfunction is a central to the pathology of diseases such as MS, epilepsy and stroke.

Infographic of the structure and associated molecules of the neurovascular unit. Image redrawn from Kadry et al., 2022 (PMID:33208141)
The BBB is made up of vascular endothelial cells with special characteristics: Tight junctions, absence of fenestrations, and active transport mechanisms.
Pericytes share a basement membrane with the endothelium.
Astrocytes extend their processes as endfeet as a direct interface between the vasculature and glia.
Tight Junctions |
Transporters |
Adherens Junctions |
 |
 |
 |
|
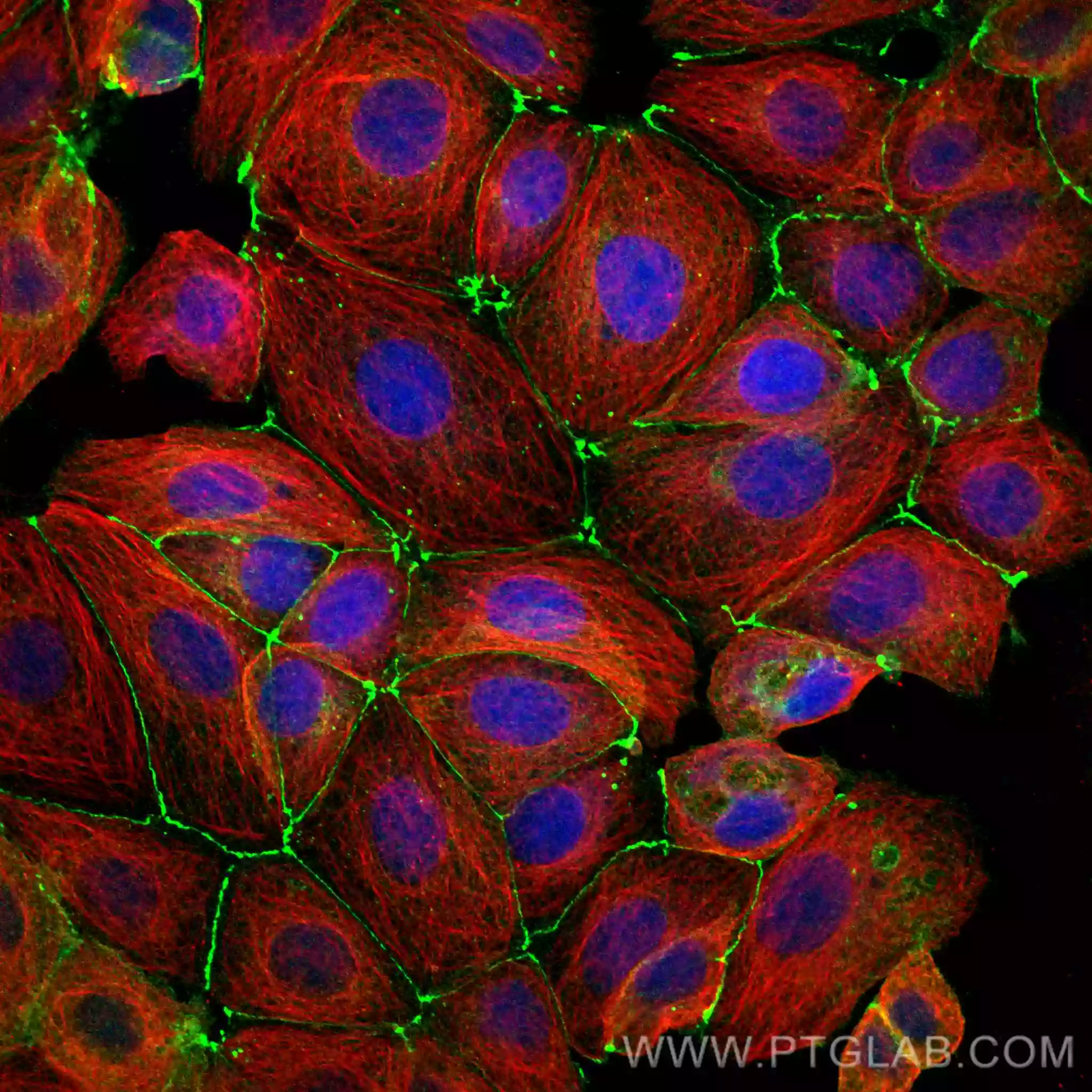
IF staining of MCF-7 cells with Occludin recombinant antibody 80545-1-RR (green), Alpha-tubulin 66031-1-Ig (red). |
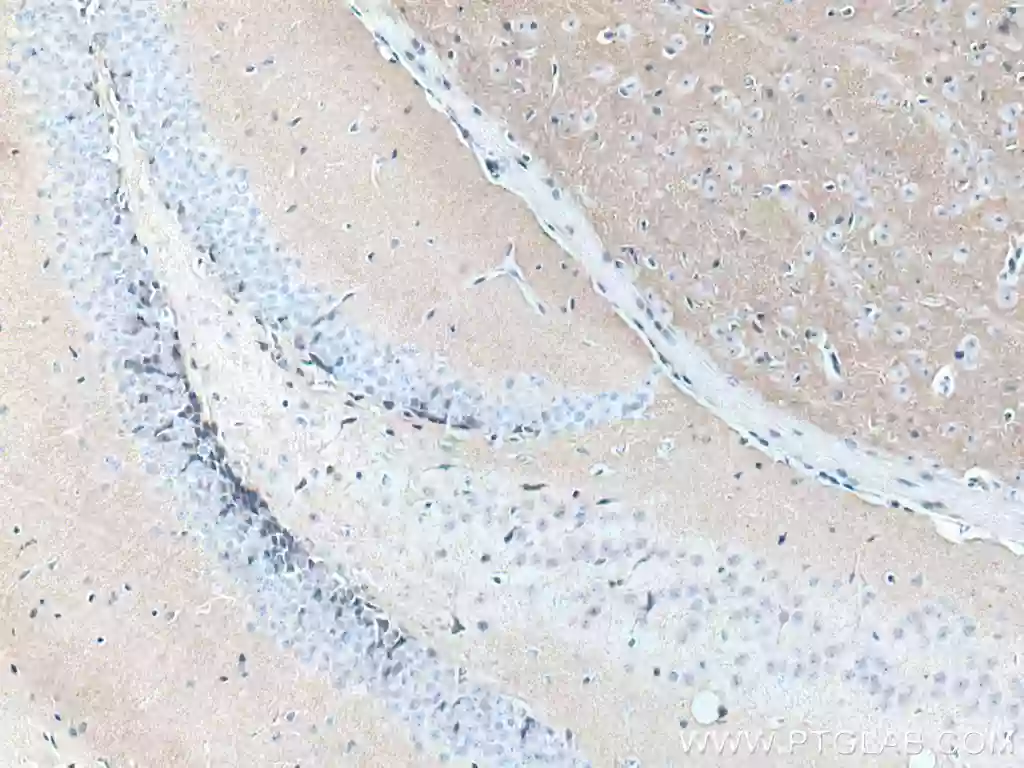
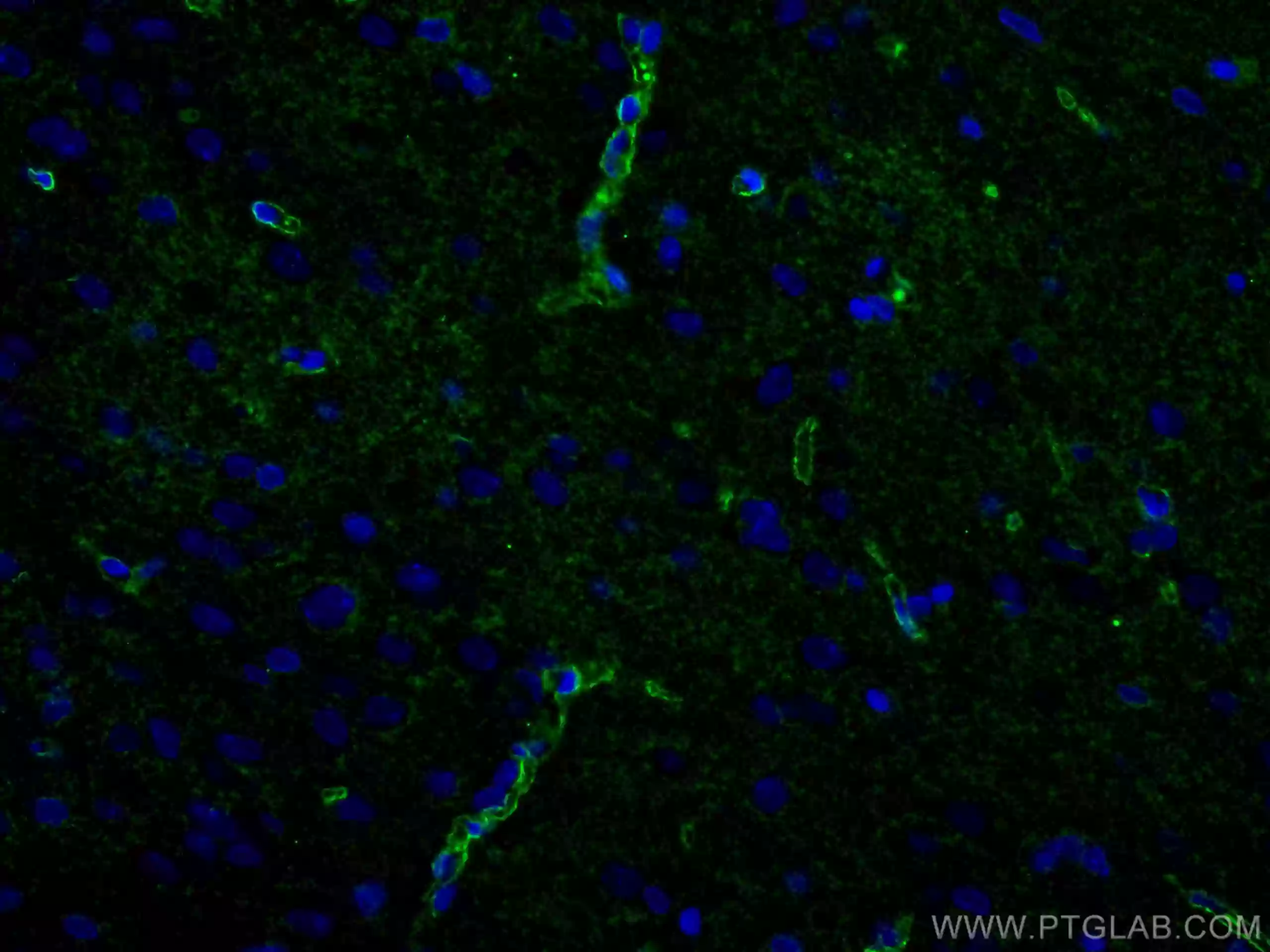
IHC staining of mouse brain tissue with N-cadherin monoclonal antibody 66219-1-Ig. |
IF analysis of rat brain with aquaporin 4 polyclonal antibody 16473-1-AP (green). |
Related Content
How to identify activated microglia
Tips to successfully culture rodent neurons

Support





