Neuronal Marker Antibodies
Proteintech offers a wide range of neuronal cell marker antibodies.
View neuronal markers catalog
|
Neuronal markers summary
Nerve cells are the basic signal components of the brain. To understand the working mechanism of the brain, we must start with the study of various types of nerve cells with different functions. The central nervous system mainly includes neurons and glial cells, of which glial cells are mainly divided into three categories: astrocytes, microglia and oligodendrocytes, each cell has unique morphological features and functions.
-
Excitatory neurons release excitatory neurotransmitters, such as glutamate and dopamine.
-
Inhibitory neurons release inhibitory neurotransmitters such as GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and glycine.
-
Dopaminergic neurons secrete dopamine, a neurotransmitter which plays an important role in many neural activities, such as mood and addiction.
-
Cholinergic neurons secrete the neurotransmitter acetylcholine which is widely distributed in the central nervous system.
-
Glial cells support and nourish neurons as well as absorb and regulate active substances.
Today many proteins have been used to identify specific neuron sub populations, such as the neuronal marker MAP2, the astrocyte marker GFAP, the oligodendrocyte marker OLIG2.
Microtubule-associated protein MAP2 is an important component of neuronal cytoskeleton and plays an important role in different stages of nervous system development, formation and regeneration. Tubulin, beta 3 is thought to be involved in the specific differentiation of neuronal cell types. TUBB3 antibodies are widely used in neurobiology.
| MAP2 Antibody |
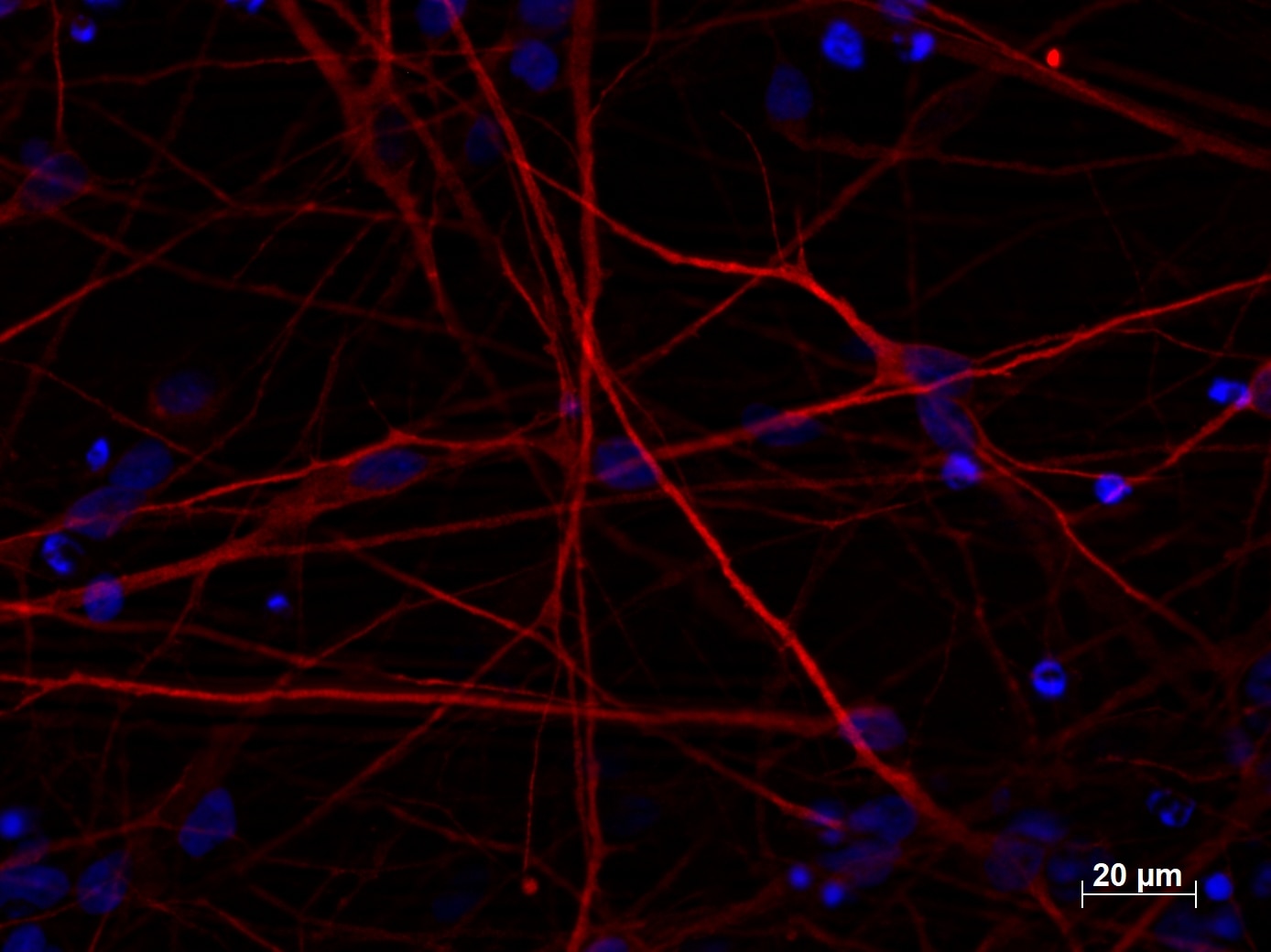 |
| Immunofluorescent staining of MAP2 (17490-1-AP, 1:250 dilution) with 4% PFA fixed control hiPSC derived neuronal cultures (35 days old). (RED MAP2; Blue: DAPI). Provided by BioTalentum Ltd., Hungary. |
| TUBB3-Specific Antibody |
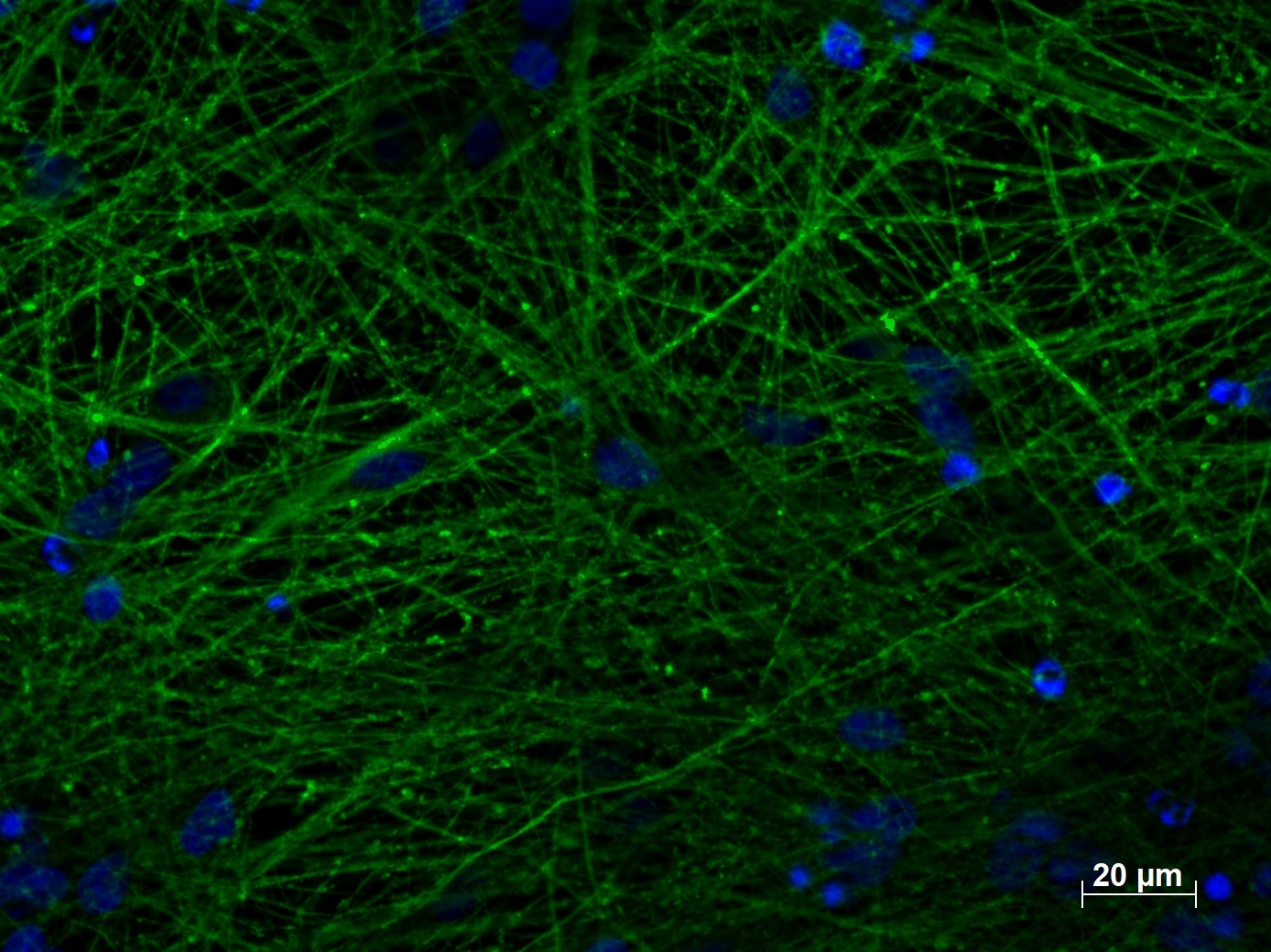 |
| Immunofluorescent staining of TUBB3 (66375-1-lg, 1:250) with 4% PFA fixed control hiPSC derived neuronal cultures (35 days old). (Green: TUBB3; Blue: DAPI). Provided by BioTalentum Ltd., Hungary. |
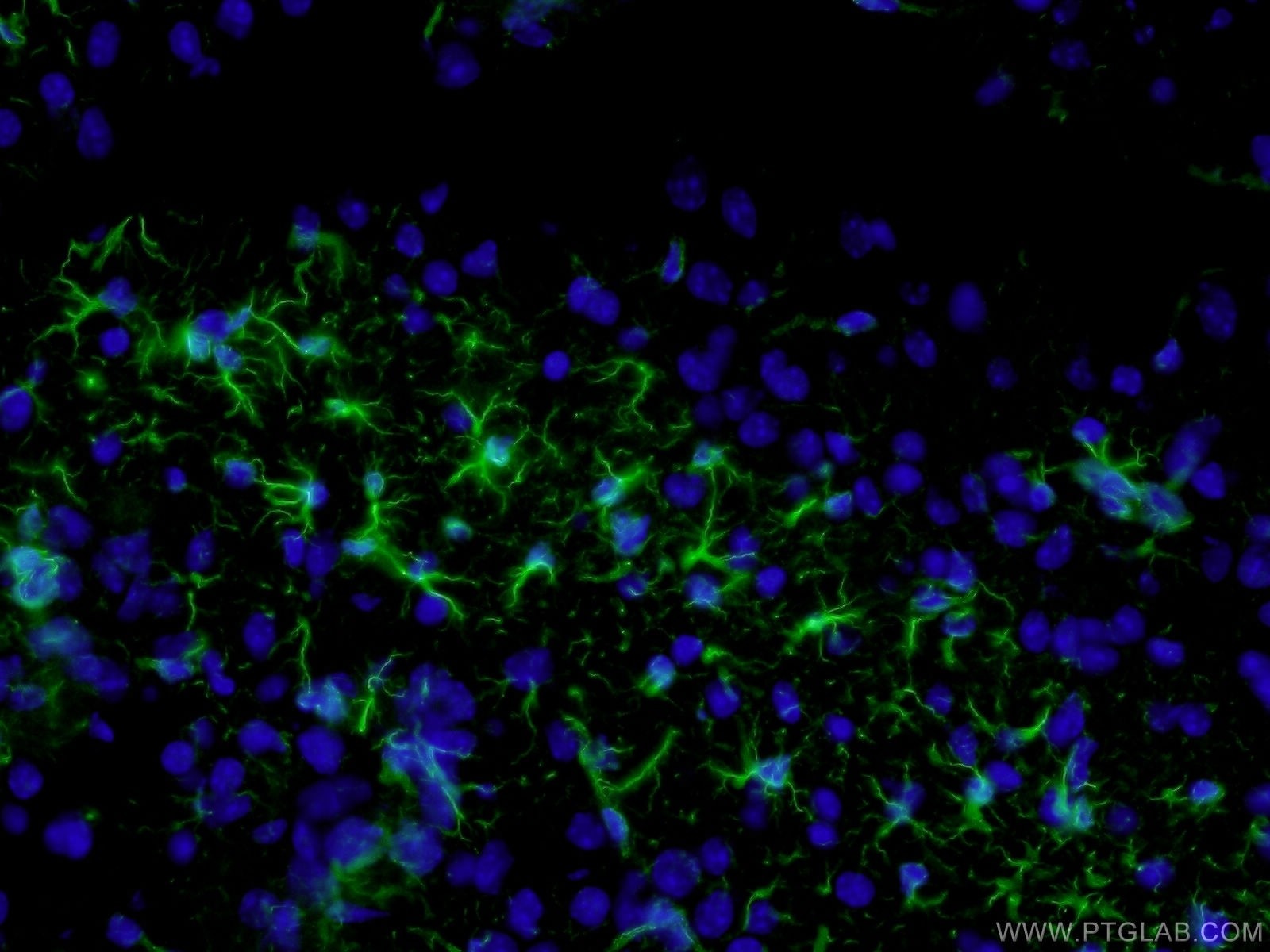 |
| Immunofluorescent analysis of ( 4% PFA ) fixed mouse brain tissue using 60190-1-Ig(GFAP antibody) at dilution of 1:100 and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Mouse IgG(H+L) |
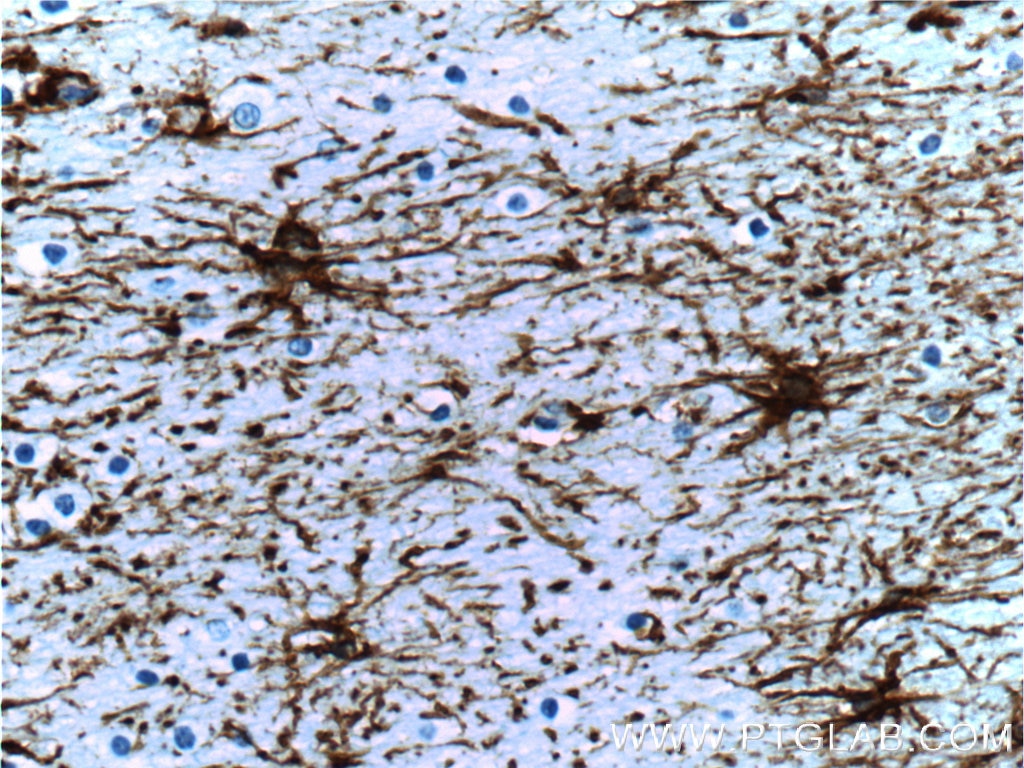 |
| Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human brain tissue slide using 60190-1-Ig( GFAP Antibody) at dilution of 1:5000 (under 40x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieved with Citric acid buffer, pH6.0. |
OLIG2: Oligodendrocyte marker
OLIG2 is a oligodendrocyte transcription factor. OLIG2 antibodies are often used as markers for oligodendrocytes in neurobiology.
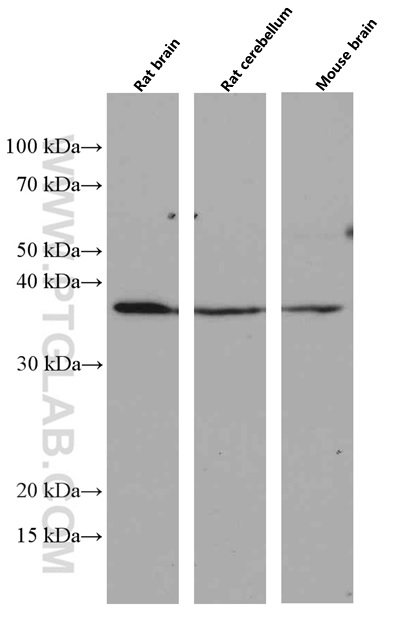 |
Various tissues were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with 66513-1-Ig (OLIG2 antibody) at dilution of 1:3000 incubated at room temperature for 1.5 hours |
Focus on WFS1
![]()
| Catalog number | Type | Applications |
| 11558-1-AP | Rabbit Polyclonal | ELISA, IHC, IP, WB |
Wolfram syndrome protein (WFS1), also known as Wolframin, is a ubiquitously expressed protein with the highest levels of expression found in the brain, pancreas, heart, and insulinoma beta-cell lines. WFS1 is involved in the regulation of calcium homeostasis, which aids in the maintenance of the endoplasmic reticulum. Mutations in the WFS1 gene are associated with Wolfram syndrome, an autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by diabetes mellitus, optic atrophy, and various additional problems involving the urinary tract, brain, and hearing.
Island and Ocean Cells
Neuroscientists based at MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology), led by Nobel Prize-winning scientist Susumu Tonegawa, have identified and characterized two types of cell in the entorhinal cortex that process the ‘when’ and ‘where’ signals in the brain - ‘island’ and ‘ocean’ cells.
Proteintech’s WFS1 Antibody in Action
Island and ocean cells are distinguishable by their expression of certain neuronal markers. Ocean cells are identifiable as reelin-positive stellate cells, (Fig.B), whereas island cells are pyramidal neurons that stain positive for WFS1, (Fig.A). Though wolframin expression is ubiquitous throughout the body, Tonegawa’s group found that it is only present in island cells in the entorhinal cortex. The group used Proteintech’s anti-WFS1 antibody (11558-1-AP) to selectively stain island cells within their research, as shown in several papers.
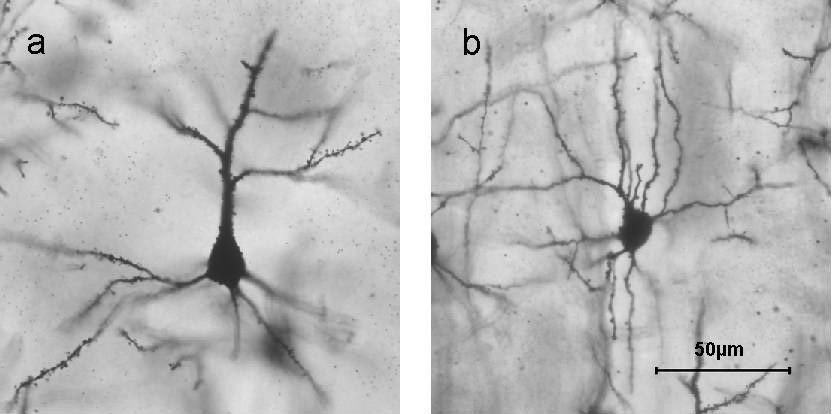 |
| Golgi stained examples of A) a pyramidal cell and B) a stellate cell. (Churchill et al. BMC Neuroscience 2004 5:43 doi:10.1186/1471-2202-5-43 Figure 1). |
Staining the two populations of cells with their specific markers allowed the Tonegawa group to map the trajectory of their connections to other parts of the brain. It became clear that island cells and ocean cells, though close in proximity, had different targets: island cells plug into the CA1 region of the hippocampus, whereas ocean cells connect to the dentate gyrus and CA3 region of the hippocampus.
Focus on IBA1
![]()
| Catalog Number | Type | Applications |
| 10904-1-AP | Rabbit Polyclonal | ELISA, IF, IHC, IP, WB |
Ionized calcium binding adapter molecule 1 (IBA1), is an inflammatory response protein expressed by monocytes and macrophages and is primarily considered a marker of macrophage activation.
IBA1 is commonly used as a marker for microglial cells. Microglial cells are resident macrophages found in the CNS and play an important role in modulating inflammatory responses within the brain. Microglia are known to scavenge both the brain and spinal cord for pathogens and cells undergoing apoptosis and aid in their removal through phagocytosis.
Activation of microglia are one of the characteristic cellular changes that occurs during neurodegenerative processes such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease. A recent study by Cui et al. has examined the etiological association between noise exposure and Alzheimer’s disease. It has long been known that Alzheimer’s disease results in neuroinflammation, therefore, Cui et al. examined the level of neuroinflammation present in the brains of mice exposed to chronic noise. Using Proteintech’s antibody IBA1 as a marker for microglia, the authors were able to detect neuroglial activation during neuroinflammation through Western blot analysis.
Furthermore. Cui et al. were able to demonstrate that when the mice were exposed to noise, the expression of IBA1 significantly increased for up to 14 days suggesting that chronic noise exposure may induce profound microglia activation, which may play a role in neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration.
As well as playing an important role in neurodegenerative disorders, IBA1 is also thought to be involved in neuropathic pain, a condition characterised by damage to the somatosensory nervous system.
A recent study by Popiolek-Barczyk et al. examined the use of the compound parthenolide on the ability to activate M2 miroglia/macrophages following sciatic nerve injury. The authors demonstrated that parthenolide increased the levels of IBA1 using our antibody alongside a reduction in pain.
IBA1 clearly plays an important role in a variety of neurological conditions including neurodegenerative processes and pain. The Proteintech IBA1 antibody has been extensively validated in-house, including specificity testing using siRNA. Furthermore, it has been used in 25 peer-reviewed publications.
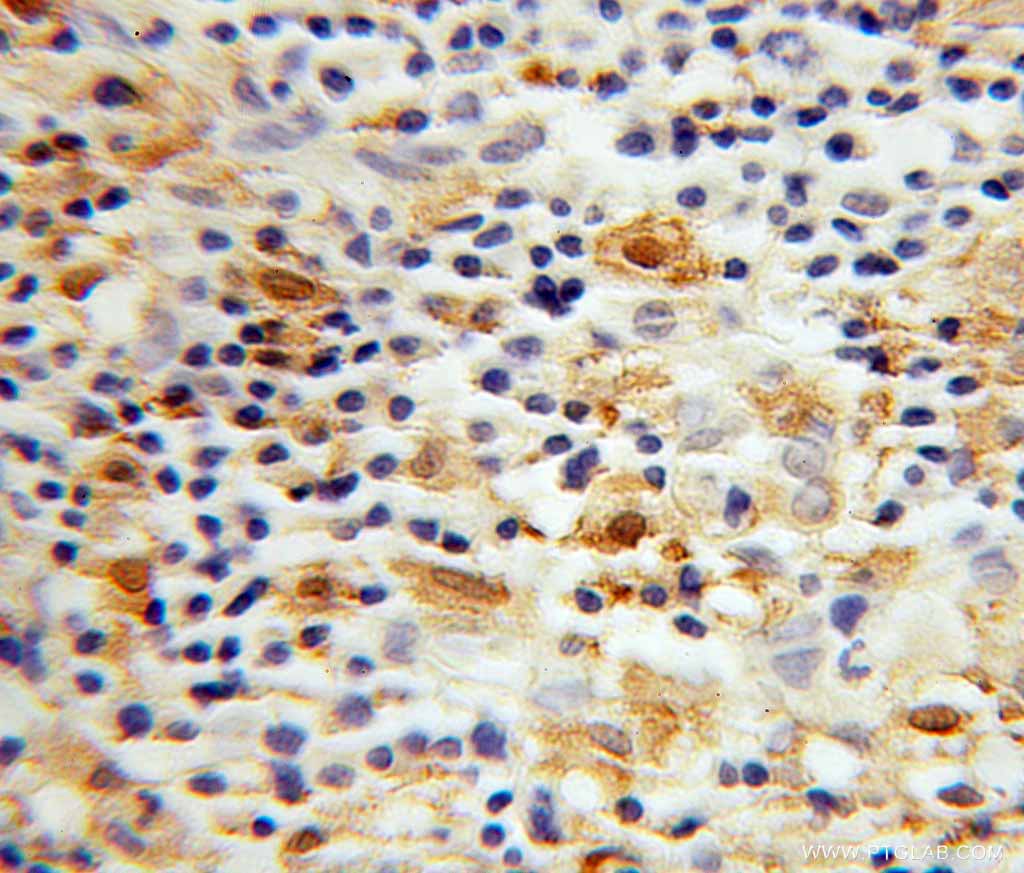 |
|
Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human lymphoma using IBA1 antibody (10904-1-AP) at dilution of 1:100 (under 40x lens). |
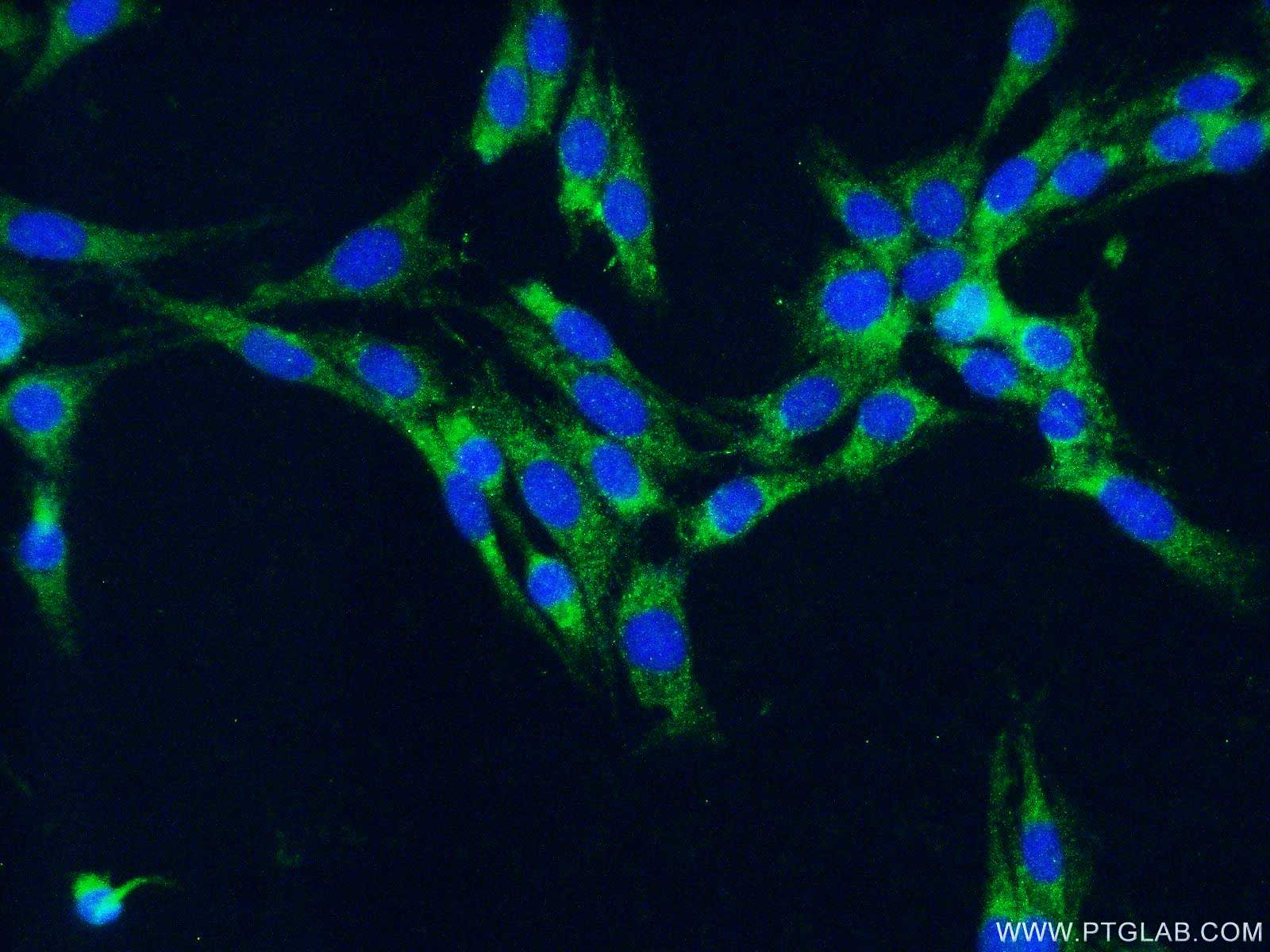 |
|
Immunofluorescent analysis of fixed C6 cells (-20ºC Ethanol) using 10904-1-AP( IBA1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:50 and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L). |
Cui B, Li K, Gai Z, et al. Chronic Noise Exposure Acts Cumulatively to Exacerbate Alzheimer’s Disease-Like Amyloid-ß Pathology and Neuroinflammation in the Rat Hippocampus. Scientific Reports. 2015;5:12943. doi:10.1038/srep12943.Popiolek-Barczyk K, Kolosowska N, Piotrowska A, et al. Parthenolide Relieves Pain and Promotes M2 Microglia/Macrophage Polarization in Rat Model of Neuropathy. Neural Plasticity. 2015;2015:676473. doi:10.1155/2015/676473.
Loading control antibodies
| GAPDH Antibody | 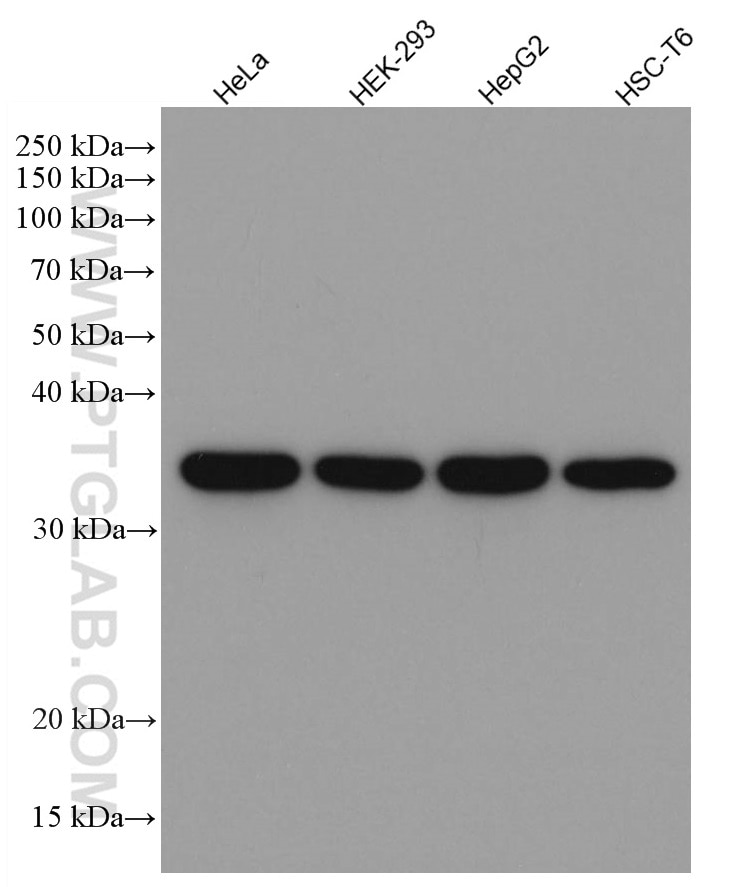 |
| Catalog no.: 60004-1-Ig | |
|
GAPDH is commonly used as a protein loading control in western blot due to its consistently high expression in most cell types. This enzyme participates in several cellular events such as glycolysis, DNA repair, and apoptosis. Proteintech monoclonal GAPDH antibodies are raised against a whole-protein antigen of human origin and have over 4,960 citations. |
| Beta Actin Antibody (KD/KO validated) | 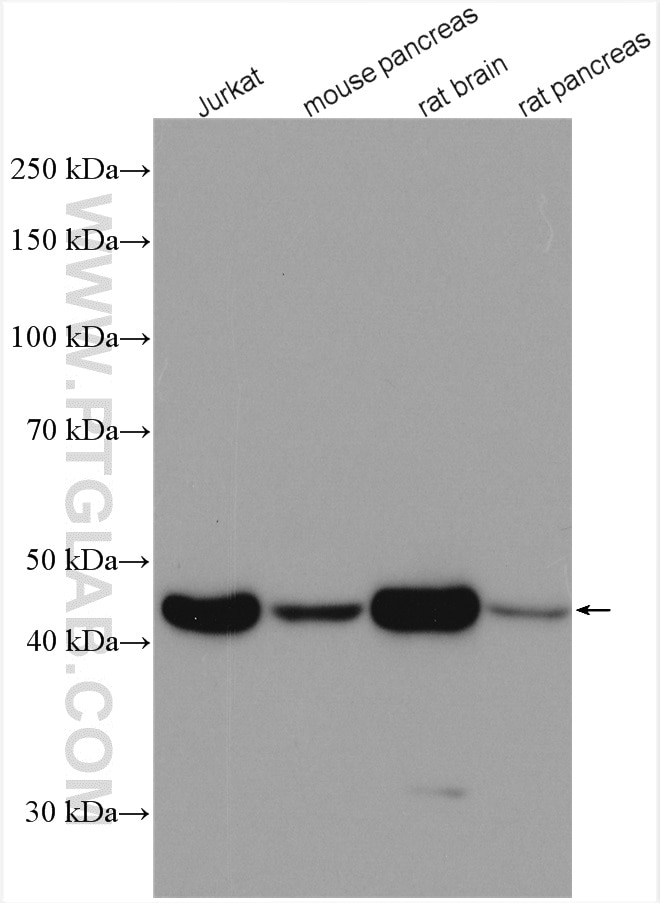 |
| Catalog no.: 66009-1-Ig | |
|
Beta-actin is usually used as a loading control due to its broad and consistent expression across all eukaryotic cell types and the fact that expression levels of this protein are not affected by most experimental treatments. 66009-1-Ig has been cited in over 2,460 publications and has wide species reactivity. |





