Ion Homeostasis Introduction
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that are present in the membranes of all cells. The main function of ion channels is the maintenance of ion gradients across the cell membrane, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals, controlling the ion flow across secretary and epithelial cells, and regulating the cell volume. Ion channels play a critical role in physiology and many different biological processes such as neuronal signal transmission, muscle contraction, or T-cell activation. Dysfunction of ion channels is the cause of several diseases and can lead to cystic fibrosis or improper functioning of the nervous system, to name just a few. Ion channels present a big opportunity for future drug therapies. Therefore, specific and selective targeting with antibodies is essential to understand their complex nature and function.
Calcium Ion Homeostasis
Calcium channels allow the passage of calcium ions in response to depolarization of the cell membrane. The accumulation of calcium can then regulate the contraction of muscles, trigger the release of neurotransmitters or hormones, modulate intracellular signaling pathways, and impact several other calcium-dependent cellular functions. Calcium channels play an important role in several diseases, such as diseases related to the cardiovascular or nervous systems.
| Catalog number |
Type |
Applications |
| 10314-1-AP |
Rabbit Polyclonal |
ELISA, IF, IHC, WB |
 |
|
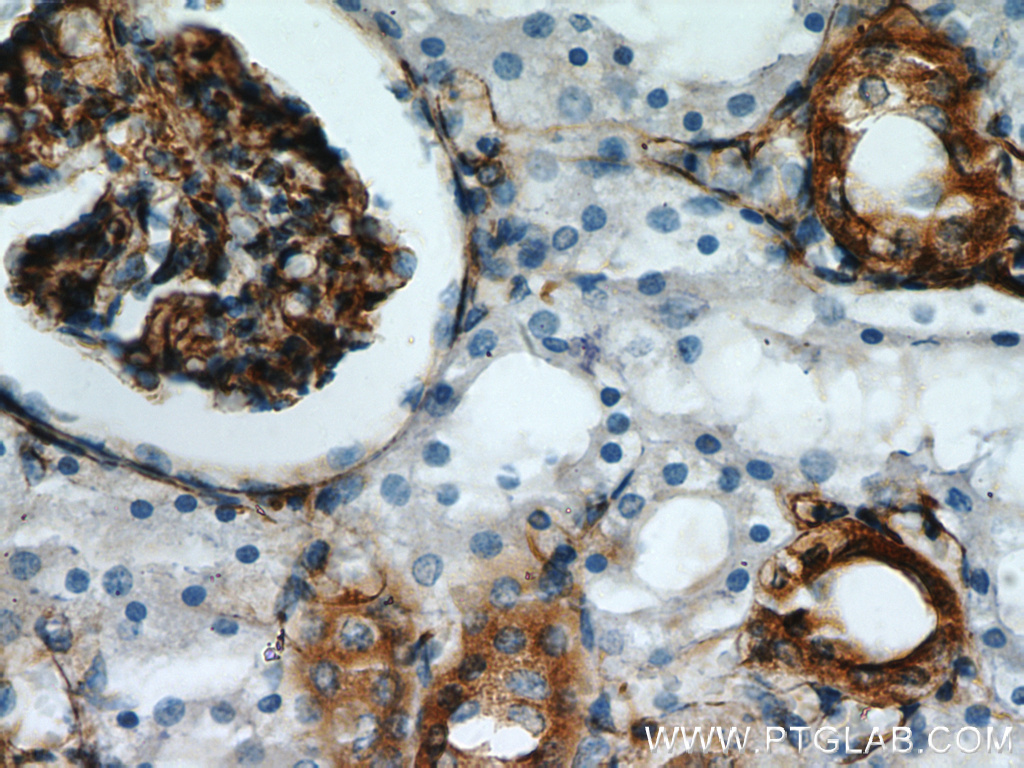
Immunohistochemical staining of paraffin-embedded human kidney using Stanniocalcin 2 antibody (10314-1-AP) at a dilution of 1:50 (10x objective).
|
|
Stanniocalcin (STC) is a family of secreted glycoprotein hormones that were originally discovered in the corpuscles of Stannius, an endocrine gland of fish. STC1 and STC2, two homologues of the STC family, are reported to be involved in calcium and phosphate homeostasis. STC is expressed in a wide variety of tissues such as the kidney, spleen, heart, and pancreas.
The protein may play a role in the regulation of renal and intestinal calcium and phosphate transport, cell metabolism, or cellular calcium/phosphate homeostasis. STC2 overexpression could promote tumor cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis in prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, or neuroblastoma. STC2 is also vital for cytoprotective properties when exposed to ER stress and hypoxia
Related Antibodies
| Antibody |
Cat no |
Type |
Applications |
| ATP1A1 |
14418-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, IHC, IP, WB |
| ATP1A1-Specific |
55187-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, FC, IF, IHC, WB |
| ATP1A2 |
16836-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, FC, IF, IHC, WB |
| ATP1A2-Specific |
55179-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, WB, IP, IHC |
| SERCA3 |
13619-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, WB, IP, IHC |
| ATP12A |
13231-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, WB |
| Calbindin-D28k |
14479-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, IF, IHC, IP, WB |
| Calretinin |
12278-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
| HRC |
18142-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, WB, IF |
Ligand-gated Ion Channels
Ligand-gated ion channels are located in the cell membrane. They open for ions to pass after binding of their ligand. Ligand binding results in a structural change to the channel and its permeability. The channel can open and ions are able to pass through.
Related Antibodies
| Antibody |
Cat no |
Type |
Applications |
| GLRA1 |
17951-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, WB, FC |
| GLRA2 |
13831-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
| GLRA3 |
13145-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, WB |
| GLRB |
15371-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, WB |
| ITPR1-Specific |
19962-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, FC, IHC, IP, WB |
| P2RX4 |
13534-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, WB, IP, IHC, IF, FC |
| P2RX5 |
19012-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, WB, IF, FC |
| Ryanodine Receptor 2 |
19765-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, IHC, WB |
| SHROOM1 |
18218-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, WB |
| Catalog number |
Type |
Applications |
| 11144-1-AP |
Rabbit Polyclonal |
ELISA, FC, IF, IHC |
 |
|
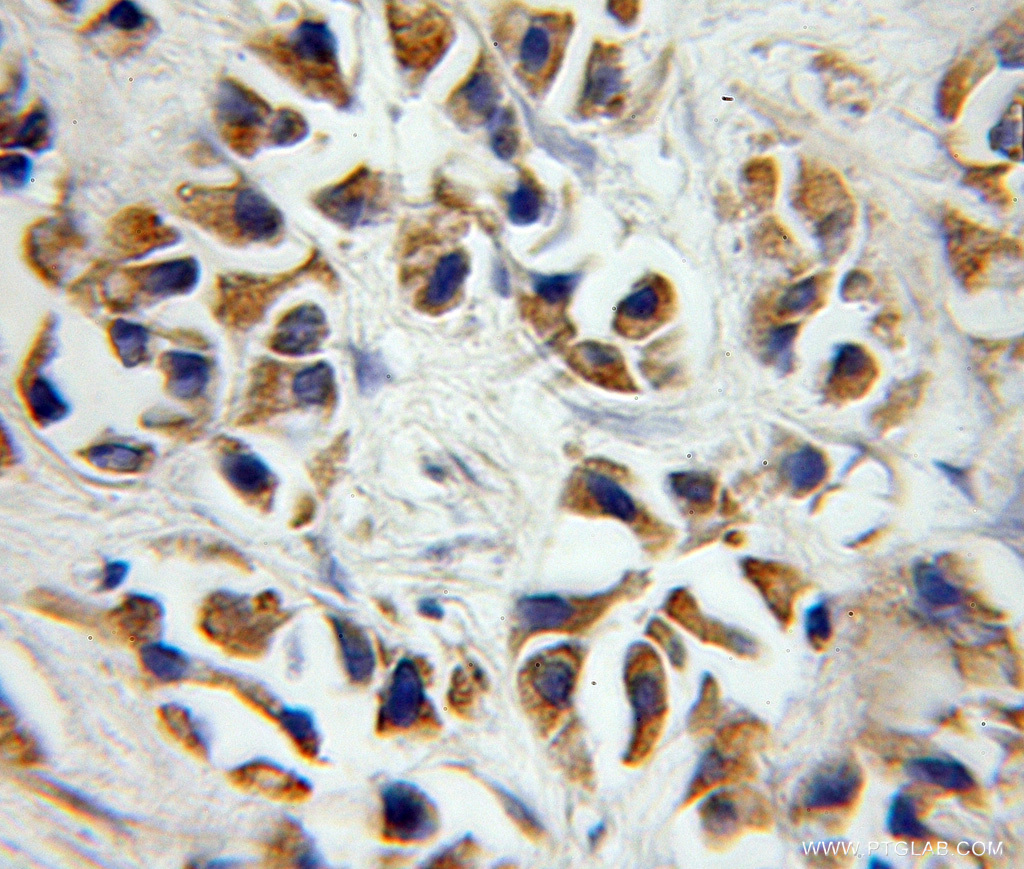
Immunohistochemical staining of paraffinembedded human prostate cancer using P2RX7 antibody (11144-1-AP) at a dilution of 1:50 (10x objective).
|
|
P2 receptors are a family of cell surface receptors that mediate a wide variety of physiologic effects in response to extracellular nucleotides. These receptors fall into two classes: P2X receptors, which are ligandgated ion channels that mediate calcium and potassium fluxes in response to ATP, and P2Y receptors, which are G-proteincoupled receptors (GPCRs).
P2RX7 functions as a ligand-gated ion channel and is responsible for ATP-dependent lysis of macrophages through the formation of membrane pores permeable to large molecules. P2RX7 is highly expressed by cells of the haemopoietic lineage and can mediate cell death, killing of infectious organisms, and regulation of the inflammatory response.
Voltage-gated Ion Channels
Voltage-gated ion channels (VDAC) open selectively for Na+, K+, Ca2+, or Cl– , whereat the voltage-gated K+ channels display the most diverse subtype. Alterations in the voltage across the membrane can open or close the channels. VDACs are present in all neurons, especially the sodium and potassium channels along the axons, which play a fundamental role in the generation of action potential and signaling between neurons.
Related Antibodies
| Antibody |
Cat no |
Type |
Applications |
| TRPA1 |
19124-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, FC, WB |
| VDAC1 |
55259-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, FC, IHC, IP, WB |
| VDAC2 |
11663-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, IHC, IP, WB |
| VDAC3 |
14451-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, IHC, WB |
| Catalog number |
Type |
Applications |
| 10866-1-AP |
Rabbit Polyclonal |
ELISA, IF, IHC, IP, WB |
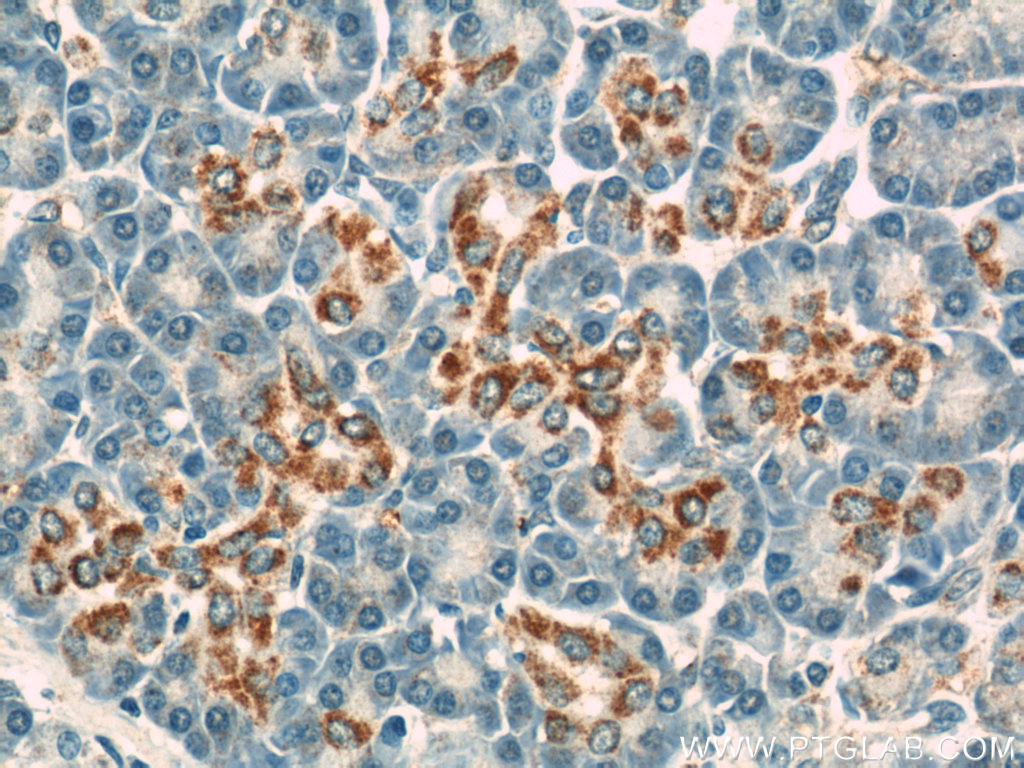 |
| Immunohistochemical staining of paraffin-embedded human pancreas using VDAC1/Porin antibody (10866-1-AP) at a dilution of 1:50 (40x objective). |
|
VDAC1, also known as VDAC, Porin 31HM, Porin 31HL, and Plasmalemmal porin, belongs to the eukaryotic mitochondrial porin family. It adopts an open conformation at low or zero membrane potential and a closed conformation at potentials above 30-40 mV, to form a channel through the mitochondrial outer membrane and also the plasma membrane. Unlike other membrane transport proteins, porins are large enough to allow passive diffusion. It is a 31kd membrane protein conserved in chimpanzee, dog, cow, mouse, rat, chicken, and zebrafish.
Cyclic Nucleotide-gated Ion Channels
Cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channels belong to the family of voltagegated ion channels. CNGs open after direct binding of cyclic nucleotides, cAMP, and cGMP. CNG channels are nonselective cation channels that poorly discriminate between alkali ions and even allow the passage of divalent cations.
Related Antibodies
| Antibody |
Cat no |
Type |
Applications |
| CNGA3 |
21657-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, WB, IP |
| HCN3 |
13745-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, WB |
| HCN4 |
55224-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, WB |
| HCN1 |
55222-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, IHC, IP, WB |
More Antibodies Related To Diverse Ion Channels
| Catalog number |
Type |
Applications |
| 10924-2-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, IF, IHC, WB |
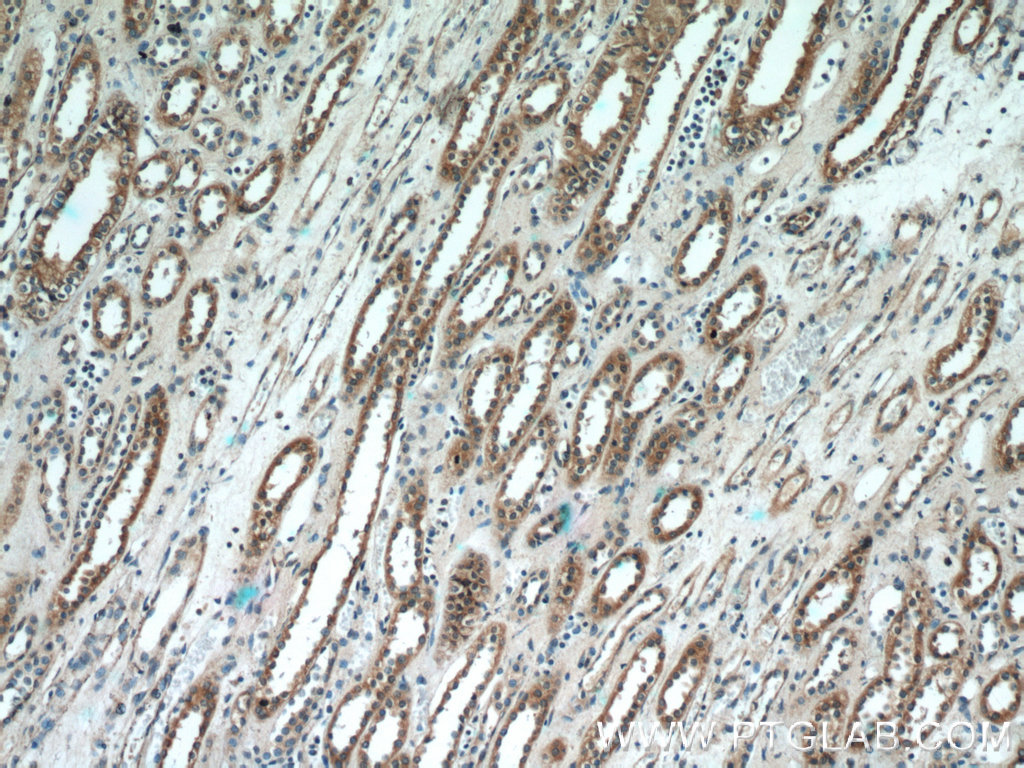 |
| Immunohistochemical staining of paraffin-embedded human kidney tissue slide using SCNN1A antibody (10924-2-AP) at a dilution of 1:50 (10x objective). |
|
SCNN1A (sodium channel, non-voltage-gated 1 alpha), also known as ENaCA (epithelial Na(+) channel subunit alpha) or amiloride-sensitive sodium channel subunit alpha, is the alpha subunit of the epithelial Na(+) channel (ENaC). ENaC is expressed in the apical membrane of salt-absorbing epithelia of kidney, distal colon, and lung. ENaC is a non-voltage-gated, constitutively active channel highly selective for sodium. It has an essential role in salt and fluid homeostasis across epithelial tissues. ENaC consists of three different subunits: alpha, beta, and gamma.
Mutations in the gene of SCNN1A have been associated with pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1 (PHA1), a rare salt-wasting disease resulting from target organ unresponsiveness to mineralocorticoids.
| Catalog number |
Type |
Applications |
| 17115-1-AP |
Rabbit Poly |
ELISA, WB, IP, IHC |
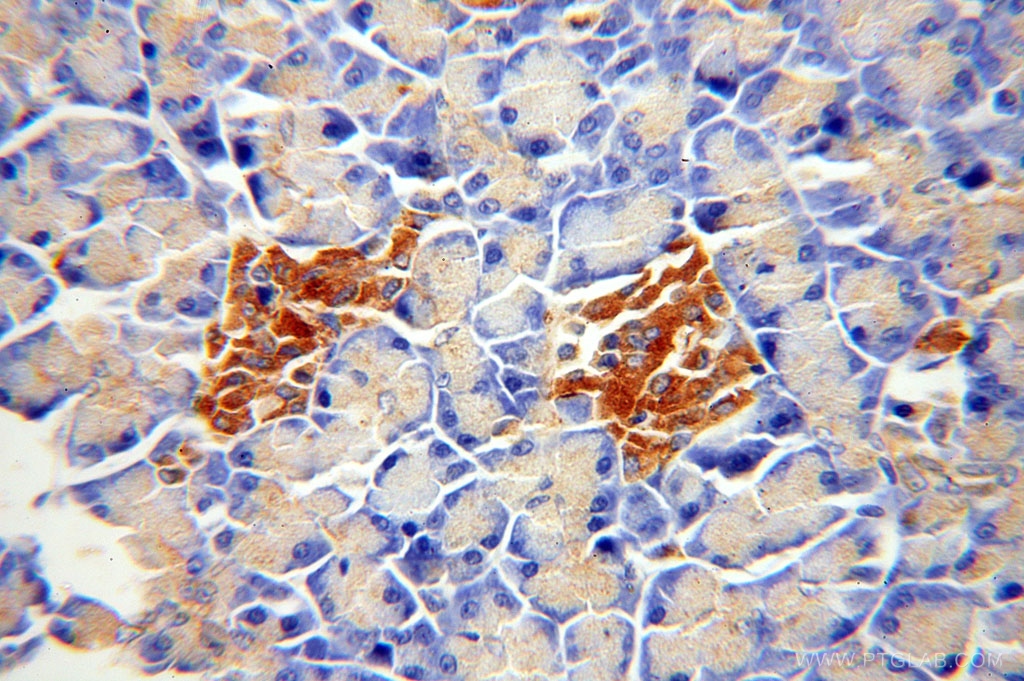 |
| Immunohistochemical staining of paraffin-embedded human pancreas using ATP6V1A antibody (17115-1-AP) at a dilution of 1:100 (40x objective). |
|
The vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPase (V-ATPase) is responsible for the acidification of endosomes, lysosomes, and other intracellular organelles. It is also involved in hydrogen ion transport across the plasma membrane into the extracellular space. The V-ATPase is a multisubunit complex with cytosolic and transmembrane domains. The cytosolic catalytic domain consists of 3 A subunits and 3 B subunits, which bind and hydrolyze ATP, as well as regulatory accessory subunits. ATP6V1A is a V-type proton ATPase catalytic subunit A.












