ANTIBODIES FOR NEURO-RELATED DISEASES: ALS AND FTD
Frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): a short tale of two neurodegenerative diseases.
Introduction
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Alzheimer’s disease (AD), frontotemporal dementia (FTD), Huntington’s disease (HD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA), and spinal muscular atrophies (SMAs), are incurable and debilitating disorders.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
ALS (also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease) is a common adult-onset neuropathological disease. Typical symptoms include hand and leg weakness, loss of ability to initiate/control movements, and slurred speech. This disorder is marked by the loss of motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord, and atrophy of the frontal and temporal lobes.
The majority of pathogenic mutations are present in TDP43 (also known as TAR DNA-binding protein 43 or TARDBP), fused in sarcoma (FUS; Figure 1), ubiquilin2 (UBQLN2; Figure 2), SOD1 (Figure 3), and also in the non-coding region of C9orf72.
|
|
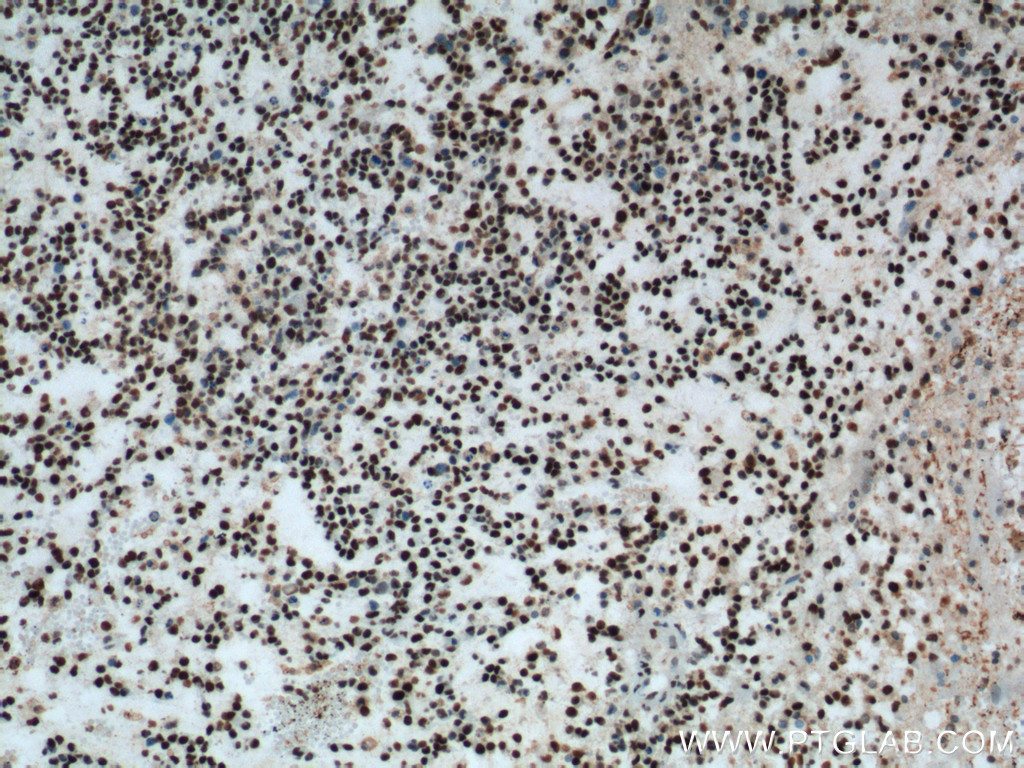
| Figure 1. Immunohistochemical staining of paraffin-embedded human gliomas tissue slide using 60160-1-Ig (FUS/TLS monoclonal antibody) at a dilution of 1:1000 (under 10x lens). A heat mediated antigen retrieval step was performed with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH9). |
|
|
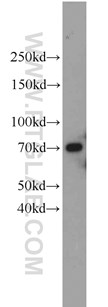
| Figure 2. Rat brain tissue lysate was subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with 23449-1-AP (UBQLN2 antibody) at a dilution of 1:800 incubated at room temperature for 1.5 hours. |
|
|
| Figure 3. Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human testis using 10269-1-AP (SOD1 antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 10x lens). |
Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD)
FTD is a disease caused by progressive nerve cell loss. The majority of cases have brain atrophy in the frontal and/or temporal lobes. FTD is known as young-onset dementia and is characterized by behavioral abnormalities including a decline in cognitive, motor, and language function.
Most common FTD mutations are related to the TARDBP/TDP-43 protein (Figure 4), TAU (Figure 5) pathology, or the fused in sarcoma (FUS) gene.
C9ORF72 IN FTD AND ALS
ALS and FTD have been classified as belonging to the same family spectrum diseases, where hexanucleotide repeat expansions (HRE) of GGGGCC in C9orf72 is a key genetic cause player. Recent studies by Davidson Y et al. have confirmed the high specificity of Proteintech C9orf72 antibodies, highlighting their great value for research and diagnostic purposes.
|
|
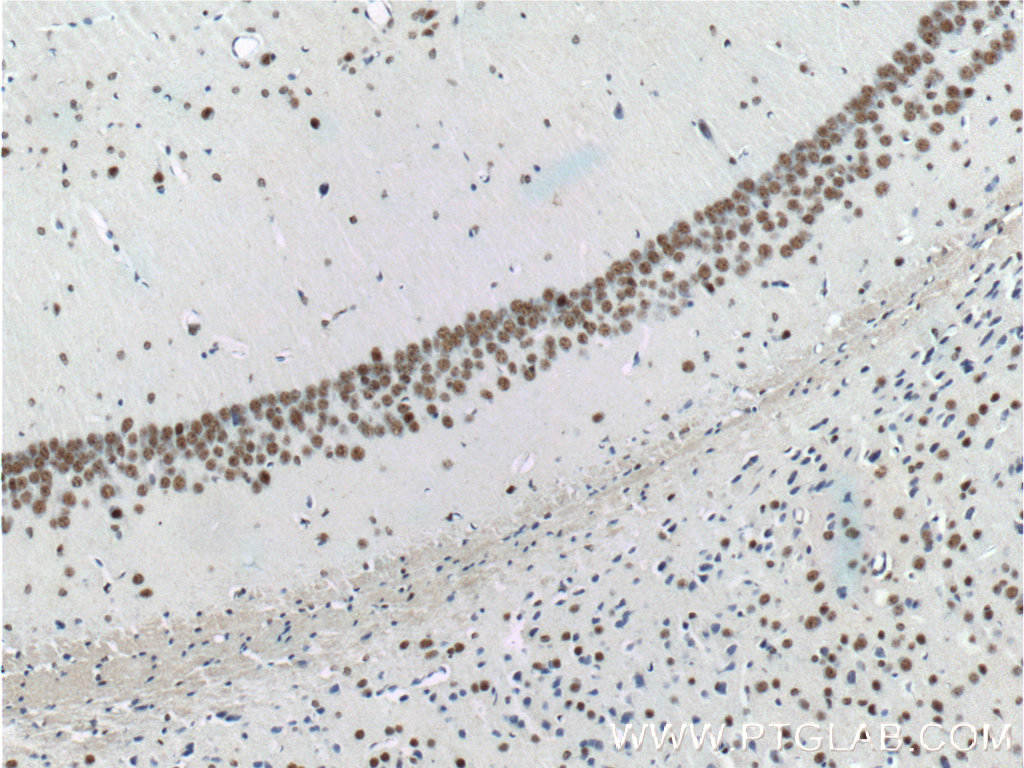
| Figure 4. Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded mouse brain tissue slide using 10782-2-AP (TDP43 antibody) at a dilution of 1:200 (under 10x lens). |
|
|
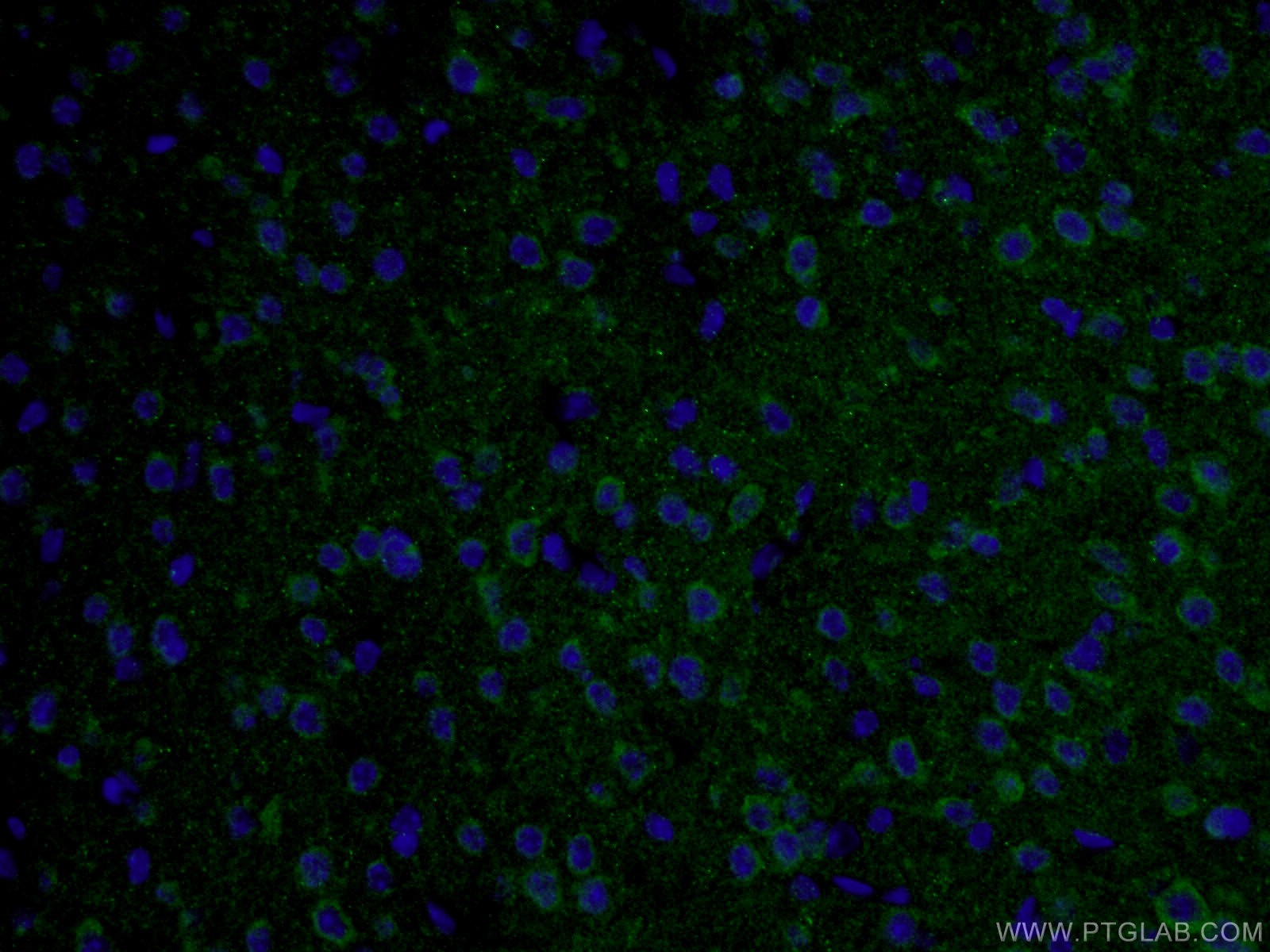
| Figure 5. Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed mouse brain tissue using 10274-1-AP (TAU antibody) at a dilution of 1:50 and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L). |
Related Antibodies
| Product | Type | Applications |
| TDP43 (C-Terminal) Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal, KD/KO validated | WB, IP, IHC, IF, chIP, ELISA |
| TDP43 (Human Specific) Antibody | Mouse monoclonal | WB, IP, IHC, FC, CoIP, ELISA |
| Recombinant TDP43 Antibody | Rabbit recombinant, KD/KO validated | WB, IHC, FC, ELISA |
| FUS/TLS Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal, KD/KO validated | WB, IP, IHC, IF, FC, chIP, ELISA |
| OPTN Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal, KD/KO validated | WB, IP, IHC, IF, FC, ELISA |
| GFAP Antibody | Mouse monoclonal | WB, IP, IHC, ELISA |
| PTEN Antibody | Mouse monoclonal | WB, IHC, IF, ELISA |
| C9orf72 Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal, KD/KO validated | WB, IP, IHC, IF, ELISA |
| VAPB Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal, KD/KO validated | WB, IP, IHC, IF, FC, ELISA |
| Ataxin 2 Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal, KD/KO validated | WB, IP, IHC, IF, ELISA |
| GR Repeat Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal | WB, IHC, IF, Dot blot, ELISA |
| GP Repeat Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal | WB, IHC, IF, ELISA |
| PR Repeat Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal | WB, IHC, IF, ELISA |
| P62/SQSTM1 Antibody | Mouse monoclonal, KD/KO validated | WB, IHC, IF, FC, ELISA |
| Granulin Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal, KD/KO validated | WB, IP, IHC, IF, ELISA |
| CHMP2B Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal, KD/KO validated | WB, IHC, IF, ELISA |
| Profilin 1 Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal | WB, IHC, IF, ELISA |
| VCP Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal, KD/KO validated | WB, IP, IHC, IF, CoIP, ELISA |
| GA Repeat Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal | WB, IHC, IF, ELISA |
| AP Repeat Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal | WB, IHC, IF, ELISA |
| TMEM106B Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal | WB, IP, IHC, IF, ELISA |
| Angiogenin Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal | WB, IHC, ELISA |
| P150 Glued Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal | WB, IHC, IF, ELISA |
| VGLUT1 Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal | IHC, IF, FC, ELISA |
| VCP Antibody | Mouse monoclonal, KD/KO validated | WB, IHC, IF, ELISA |
| ALS2 Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal | WB, IP, IHC, IF, ELISA |
| VGLUT2 Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal | WB, IHC, IF, ELISA |
Final remarks
New drugs should be developed to have neuroprotection properties via the improvement of synaptic plasticity, reduced oxidant and inflammation damage, or rescue mobility dysfunctions.
With an increasingly aging global population, the economic, as well as human, impact of neurodegenerative disorders is expected to increase unless reliable tools and care strategies can be developed. For example, recently, neuronal pentraxin 2 (NPTX2) has been identified as a reliable marker in f cerebrospinal fluid to monitor the progression of FTD. NPTX2 (10889-1-AP), also known as NARP (neuronal activity-regulated pentaxin), is secreted protein involved in excitatory synapse formation. It also plays a role in the clustering of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA)-type glutamate receptors at established synapses, resulting in non-apoptotic cell death of dopaminergic nerve cells.