Markers for Immune cells
Immune markers and related antibodies
Introduction
The human immune system contains a collection of different cell types and molecules that help to protect the body from toxins, viral infections, bacteria, and parasites. Although immunology covers all aspects of this complex network, the field is united by the immune cell. The central points of immunology are: understanding, identifying, and distinguishing the many different immune cells that are essential for diagnosis and therapy. Cell markers are helpful tools used to identify a specific immune cell population. This catalog offers a detailed choice of the most commonly used cell markers and an extensive selection of antibodies used in immunology.
B Cells
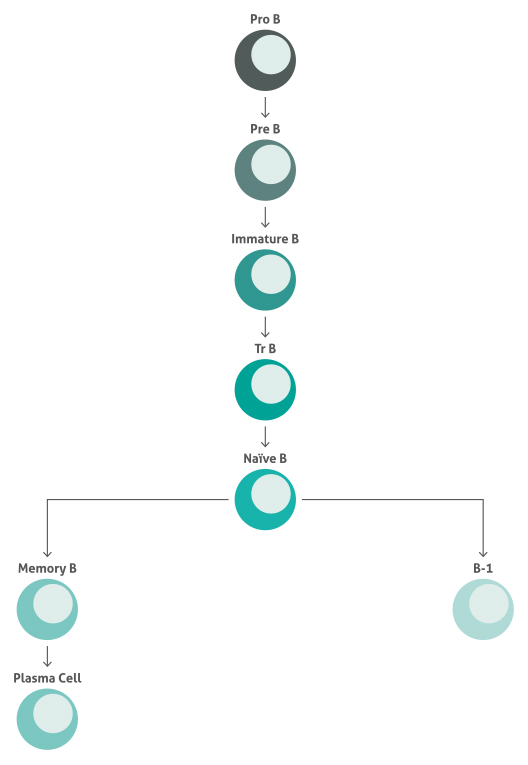
B cells (bursal or bone marrow-derived cells) are lymphocytes that play a pivotal role in the adaptive immune system and disruption of B cell function is a common hallmark of many different diseases. B cells are produced in the bone marrow and migrate to the spleen and other secondary lymphoid tissues for maturation. B cells go through several stages of development during exposure to antigens.
Maturation Of Human B Cells
Related antibodies
| Antibody | Catalog number | Type | Applications |
| CD38 | 25284-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, WB, IHC, FC |
| CD38 | 60006-1-Ig | Mouse Mono | ELISA, IF, WB |
| CD138/Syndecan-1 Antibody | 10593-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, IF, IHC, IP, WB |
| CD138/Syndecan-1 Antibody | 60185-2-Ig | Mouse Mono | ELISA, WB, IHC |
| MME,CD10 Antibody | 18008-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, WB, IP, IHC, FC |
| MME,CD10 Antibody | 60034-3-Ig | Mouse Mono | ELISA, WB, IHC |
| CD19 | PE-65145 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD19 | PE-65110 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD19 | FITC-65145 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD19 | APC-65145 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD19 | APC-65110 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD38 | APC-65111 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
CD20
CD20 is a B-lymphocyte surface molecule that is widely expressed during B-cell ontogeny, from early pre-B-cell developmental stages until final differentiation into plasma cells. It is involved in the regulation of B-cell activation and proliferation. CD20 also serves as a useful target for antibody-mediated therapeutic depletion of B cells.
| Antibody | Catalog number | Type | Applications |
| CD20 | 24828-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, FC, IHC, IP, WB |
| CD20 | 60271-1-Ig | Mouse Mono | ELISA, FC, IHC, WB |
| CD20 | PE-65085 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD20 | FITC-65085 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD20 | CL647-60271 | Mouse Mono | FC, IF, ELISA |
| CD20 | APC-65085 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
T Cells
T cells are white blood cells. They perform a variety of functions in the blood system. T cells detect cellular abnormalities, directly destroy bacterially infected cells, and support other immune cells to produce antibodies. Thus, T cells are essential for the human immune system. There are different types of T cells named helper T cell, killer T cell, and regulatory T cell (Treg). Every T cell type expresses different cell surface markers and secretes different cytokines. A short list is mentioned below and on the following page.
T Helper Cells
| Antibody | Catalog number | Type | Applications |
| CCR5 | 11056-2-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, IHC, IP, WB |
| CD4 | 17476-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, FC, WB |
| CXCR3B-specific | 60065-1-Ig | Mouse Mono | ELISA, WB |
Killer T Cells
| Antibody | Catalog number | Type | Applications |
| CD8a | 17335-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, IHC |
| CD8b | 21256-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, WB |
Monocytes and Macrophages
Macrophages (and their precursor cells, monocytes) are important cells of the immune system. Upon infection or tissue damage, monocytes, one of the major groups of white blood cells, rapidly differentiate into macrophages. Macrophages are large, specialized cells that are present in every tissue of the body. They recognize and consequently destroy the target cell. Macrophages provide a first line of defense in protecting the host from infection.
| Antibody | Catalog number | Type | Applications |
| CD11b | PE-65116 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD11b | APC-65116 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD11c | PE-65086 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD11c | FITC-65086 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD11c | APC-65086 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD11c/Integrin Alpha X | 17342-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, WB, IHC, FC |
| CD11c/Integrin Alpha X | 60258-1-Ig | Mouse Mono | ELISA, IHC, WB |
| CD14 | 17000-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, FC, IF, IHC, WB |
| CD14 | PE-65056 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD14 | FITC-65056 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD206 | 18704-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, FC, IF, IHC, WB |
Granulocytes
Granulocytes are a type of white blood cells. They comprise about 60% of all white blood cells. There are three different forms of granulocytes: basophils, eosinophils, and neutrophils. All granulocyte forms have the capacity to ingest virus particles, bacteria, or other parasites. For this reason, granulocytes contain big granules packed with enzymes that help to digest the foreign molecule.
Basophils
Basophils are a small subgroup of granulocytes. Basophils are mainly involved in defense against parasites and in response to allergic reactions. Basophils contain several surface molecules, the most representative of which are listed below.
| Antibody | Catalog number | Type | Applications |
| CD44 | PE-65063 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD44 | FITC-65063 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD44 | APC-65063 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD107a | PE-65051 | Mouse Mono | FC, IF, ELISA |
| CD107a | FITC-65051 | Mouse Mono | FC, IF, ELISA |
Eosinophils
Eosinophils, like all other granulocyte forms, destroy parasites. Besides this, eosinophils are proinflammatory cells (that are) able to produce and release toxic proteins. Hence, eosinophils are also involved in allergic reactions
| Antibody | Catalog number | Type | Applications |
| C5aR | 21316-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | FC, IF, IHC, IP, WB, ELISA |
| CD23 | 18642-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | FC, IHC, WB, ELISA |
| Integrin alpha-4 | 19676-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | FC, IHC, WB, ELISA |
Neutrophils
Neutrophils are the most common granulocyte cell type found in the blood system. They display the first defense mechanism to bacterial infection or other acute inflammations. Some markers are mentioned below.
| Antibody | Catalog number | Type | Applications |
| CD11b | PE-65116 | Mouse mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD11b | APC-65116 | Mouse mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD11c | PE-65086 | Mouse mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD11c | FITC-65086 | Mouse mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD11c | APC-65086 | Mouse mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD14 | PE-65056 | Mouse mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD14 | FITC-65056 | Mouse mono | FC, ELISA |
Dendritic Cells
Dendritic cells (DC) are potent antigen-presenting cells that are important for the induction of the primary immune response, including induction of T cell responses, migration, or antigen capture. Dendritic cells are found in different tissues and immature forms are also found in the blood. They differentiate and become active in different tissues to take up and process the antigen. In general, activated dendritic cells move to the lymph tissue to interact with T or B cells.
| Antibody | Catalog number | Type | Applications |
| CD21 | 66701-1-Ig | Mouse Mono | WB, ELISA |
| CD21 | 28206-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | IHC, ELISA |
| CD21 | 24374-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, IHC |
| CD23 | 18642-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, WB, IHC, FC |
| CD23 | CL594-60208 | Mouse Mono | IF, ELISA |
| CD23 | CL488-60208 | Mouse Mono | IF, ELISA |
| CD23 | 60208-2-Ig | Mouse Mono | IF, IHC, WB, ELISA |
| CD23 | 60208-1-Ig | Mouse Mono | IF, IHC, WB, ELISA |
| Clusterin | 12289-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, WB, IP, IHC |
| Clusterin | 66109-1-Ig | Mouse Mono | IHC, WB, ELISA |
Mast Cells
Mast cells are a type of leukocyte. They are best known for their role in mediating allergic diseases and autoimmunity. However, they also play an important role in defending against pathogens. Mast cells are found in most tissues of the body, especially in areas that are in contact with the external environment such as the skin or intestine. In their immature form, mast cells circulate in the blood. Mast cells contain several inflammatory factors, lipid mediators, and many more factors. Upon stimulation, they degranulate and release different mediators, which in turn modulates the host’s innate immune system.
| Antibody | Catalog number | Type | Applications |
| CD9 | PE-65070 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD9 | FITC-65070 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD25 | PE-65096 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD25 | APC-65096 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD33 | 17425-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC |
| CD44 | PE-65063 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD44 | FITC-65063 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD44 | APC-65063 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| Integrin alpha-4 | 19676-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, IHC, WB |
| Integrin beta-1 | 12594-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, IHC, WB |
| Transferrin receptor/ CD71 | 10084-2-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, IF, IHC, IP, WB |
CD44
CD44 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein that mediates cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions through its affinity for hyaluronic acid (HA) and possibly also through its affinity for other ligands.
Adhesion with HA plays an important role in cell migration and tumor growth. CD44 is also involved in lymphocyte activation, recirculation and homing, and in hematopoiesis.
| Antibody | Catalog number | Type | Applications |
| CD44 | 15675-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, FC, IF, IHC, IP, WB |
| CD44 | 60224-1-Ig | Mouse Mono | ELISA, FC, IF, IHC, WB |
Megakaryocytes
Megakaryocytes are rare myeloid cells found primarily in the bone marrow. Megakaryocytes produce thrombocytes, which are essential for normal blood clotting. The formation of platelets requires several intrinsic series of remodeling events of the megakaryocytes that result in the release of thousands of platelets from one single megakaryocyte.
| Antibody | Catalog number | Type | Applications |
| CD36 | 66395-1-Ig | Mouse Mono | IHC, WB, ELISA |
| CD41/Integrin alpha 2b | 60350-1-Ig | Mouse Mono | WB, ELISA |
| CD41/Integrin alpha 2b | 24552-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | IHC, IP, WB, ELISA |
| CD41/Integrin alpha 2b | 18308-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | IHC, ELISA |
| CD42b | 12860-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, IHC, IP, WB |
| GP9 | 67271-1-Ig | Mouse Mono | IHC, WB, ELISA |
| GP9 | 14564-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | IHC, WB, ELISA |
| Integrin beta-3 | 18309-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, IHC, WB |
| Integrin beta-3 | 66952-1-Ig | Mouse Mono | WB, ELISA |
| P-selectin | 60322-1-Ig | Mouse Mono | IHC, IP, WB, ELISA |
| P-selectin | 13304-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | IHC, WB, ELISA |
NK Cells
Natural killer (NK) cells are lymphocytes that are essential in the innate immune system. They are important especially for the destruction of cells infected by a virus or of tumor cells. NK cells kill infected cells by releasing small cytoplasmic granules that trigger cell death (apoptosis).
| Antibody | Catalog number | Type | Application |
| CD11c | PE-65086 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD11c | FITC-65086 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD11c | APC-65086 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD16 | PE-65090 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD56 | PE-65067 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD56 | FITC-65067 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
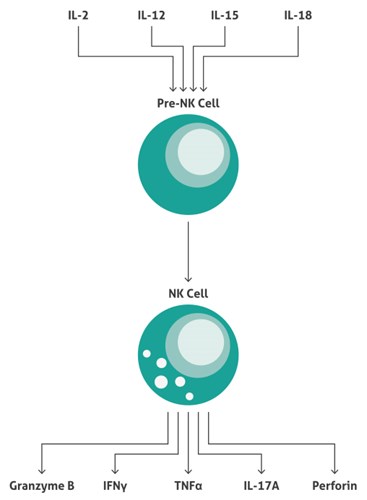
Maturation Of Natural Killer Cells
The pre-NK cell gets activated in response to, e.g., IL-2, IL-12, IL-15, or IL-18. The NK cell then produces and secretes several cytokines, chemokines, and cell death-inducing proteins.
| Antibody | Catalog number | Type | Application |
| CD11c/Integrin Alpha X | 17342-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, WB, IHC, FC |
| CD11c/Integrin Alpha X | 60258-1-Ig | Mouse Mono | ELISA, IHC, WB |
| GZMB | 13588-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, IF, IHC, WB |
Erythrocyte
Erythrocytes (also known as red blood cells) are the most common cell type in the blood system. They are essential for the delivery of oxygen from the lungs to body tissue. Mature erythrocytes do not have a nucleus and lack most organelles. They are of flexible shape, thus flowing easily through the blood circulation.
| Antibody | Catalog number | Type | Applications |
| HBE1-Specific | FITC-66151 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| HBE1-Specific | 66151-1-Ig | Mouse Mono | FC, IHC, WB, ELISA |
| Glycophorin A | 15874-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | FC, IHC, WB, ELISA |
| Hemoglobin epsilon | 12361-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | FC, IHC, WB, ELISA |
Myeloid-derived Suppressor Cells
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) form a very heterogeneous cell population. MDSCs are of great interest as they expand during cancer, inflammation, or infection. In addition, they have not only the ability to secrete immunosuppressive cytokines that regulate T cell function, but they also have the capacity to suppress the cytotoxic effects of natural killer cells.
| Antibody | Catalog number | Type | Applications |
| CD11b | PE-65116 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD11b | APC-65116 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD11B/ Integrin alpha M | 20991-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, FC, IHC, WB |
| CD14 | FITC-65056 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD14 | APC-65116 | Mouse Mono | FC, ELISA |
| CD33 | 17425-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, FC, IF, IP, WB |
| VEGFR-1/FLT-1 | 13687-1-AP | Rabbit Poly | ELISA, IP, WB |






